Greece votes 'no' in bailout referendum, putting eurozone membership in peril
European leaders call emergency meeting after overwhelming rejection of austerity measures
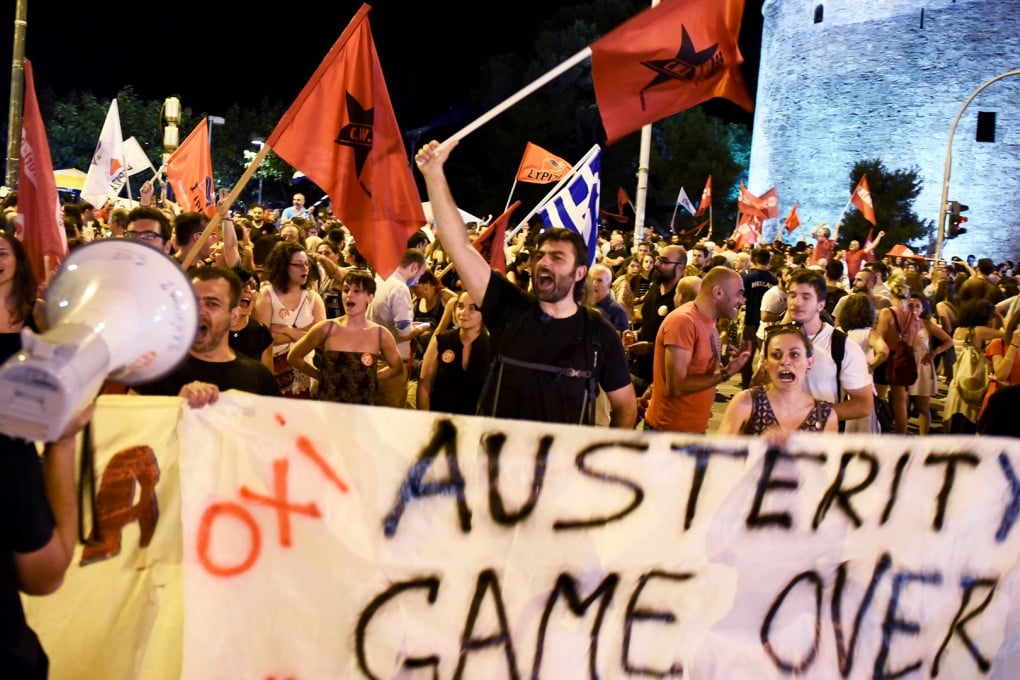
Greeks overwhelmingly rejected conditions of a rescue package from creditors on Sunday, throwing the future of the country's eurozone membership into further doubt and deepening a standoff with lenders.
As the euro slid more than 1 percent against the dollar and European stock and bond markets were poised to take a sharp hit with the resumption of trade on Monday, stunned European leaders called a summit for Tuesday to discuss their next move.
Thousands of jubilant Greeks waving flags and bursting fire crackers poured into Athens' central square as official figures showed 61 percent of Greeks had rejected a deal that would have imposed more austerity measures on an already ravaged economy.
"You made a very brave choice," Prime Minister Alexis Tsipras said in a televised address. "The mandate you gave me is not the mandate of a rupture with Europe, but a mandate to strengthen our negotiating position to seek a viable solution."
The surprisingly strong victory by the 'No' camp defied opinion polls that had predicted a tight contest after a week of rising desperation as banks shut and cash machines ran dry.