China EV war: investors curb their enthusiasm for NIO, Xpeng, other Tesla rivals as earnings test follows US$124 billion market drubbing
- Market pacesetters NIO, Xpeng, Li Auto face a myriad of challenges with losses still to snowball in 2021 and analysts grow weary of short-term outlook
- Automotive chip shortage will add to other lingering market concerns about US-listed Chinese stocks and outlook for central bank policy tightening
“In the short term, market volatility will continue to add downside risk to valuations,” said Shen Dai, an analyst at SPDB International, the overseas investment banking unit of Shanghai Pudong Development Bank, which has a sell rating on the NEV sector. “We advise investors to remain cautious because of the valuation and the impact of the supply chain.”
A weak 2020 earnings report and a dividend cut from Geely Auto on March 23 sent the stock tumbling by 15 per cent in Hong Kong last week. Net income trailed market consensus by a wide 23 per cent despite an industry rebound. BYD will come up next, with its fourth quarter results on Monday.
Geely fell 2.6 per cent to HK$19.92 in early trading on Monday, while BYD lost 1.9 per cent to HK$173.70.
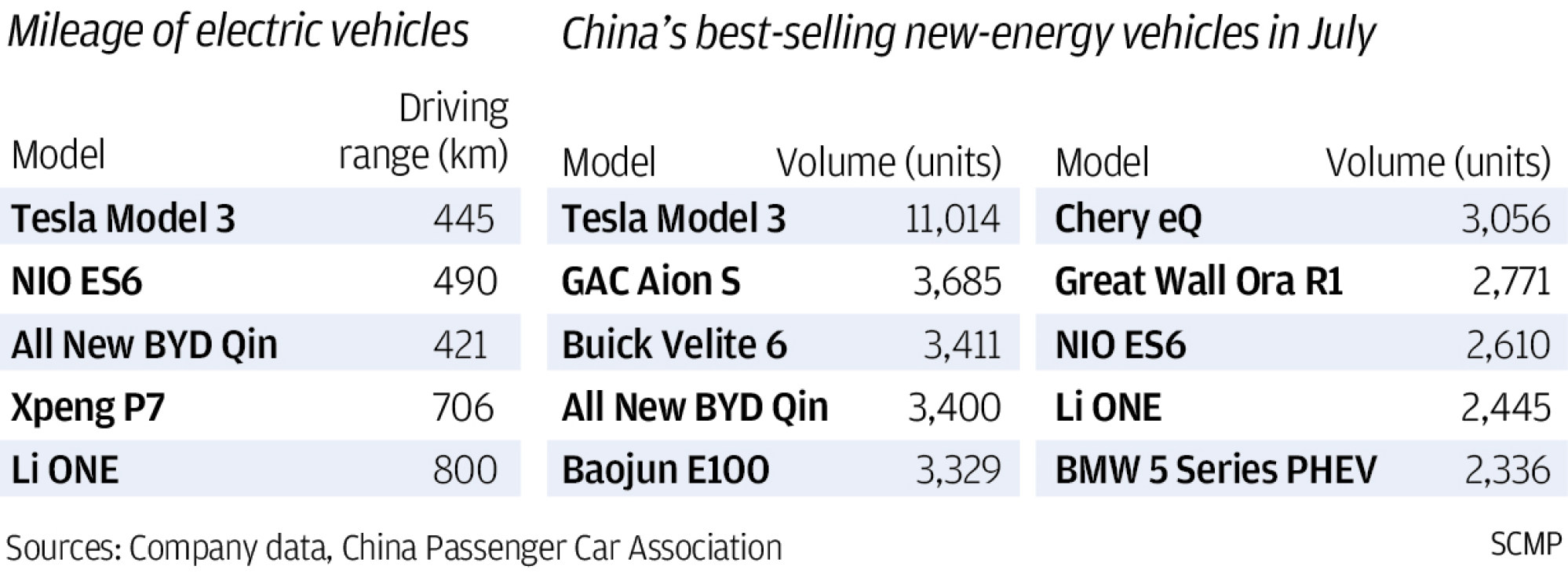
Tesla currently dominates China’s premium electric-car niche market, delivering nearly 140,000 Shanghai-made Model 3 sedans last year. China’s electric passenger-car market grew 19 per cent to 1.24 million in 2020, according to Statista, more than three times the next biggest market in Germany.
China is aiming for 20 per cent of the country’s new cars to be powered by clean energy by 2025, or more than 40 million units.
The trio chalked up a combined annual loss of 11.2 billion yuan in 2020 and will start reporting their first-quarter 2021 earnings in late May.
“The penetration rate of new-energy vehicles is only around 7 per cent in China and there’s huge potential for expansion,” said Wang Jing, an analyst at Zheshang Securities. “But earnings will be what the market is focusing on heading into 2021. Buying needs to be selective on the core assets in the sector.”
The loss projections will add to already sour sentiment in the sector, one of the stampede trades involving liquor distillers, technology disrupters and clean-energy companies. Production hiccup has added to ongoing concerns about policy normalisation by global central banks and worsening US-China relations.
Shares of NIO, Xpeng, Li Auto, Geely and BYD have slumped by 32 per cent to 43 per cent from their highest levels this year, resulting in a cumulative US$124 billion erosion in their market values, according to Bloomberg data. They are still “overbought”, according to BCA Research in a March 24 report.
Chinese NEV makers and NEV battery producers will deliver considerable positive long-term returns, they added. The basis for this assumption is that many of them will experience strong revenue growth over this decade, according to the report.
BCA Research forecasts NEV share of China’s total vehicle sales is likely to rise significantly to 40 per cent in 2030, from only 5.4 per cent in 2020. This will translate into a compound annual growth rate of 24 to 25 per cent in Chinese NEV this decade.
“While NEV maker stock prices have recently fallen considerably, we think they are still overpriced and recommend waiting for a better entry point,” analysts led by Ellen JingYuan He said. The Chinese NEV makers “could be a good long-term investment,” they added, without mentioning individual stocks.


