Explainer | How are China-Kazakhstan relations, and how strategically important is the Central Asian nation to Russia, the US and Europe?
- Chinese President Xi Jinping will visit Kazakhstan on his first overseas trip since the start of the coronavirus pandemic next week
- Strategically located between China and Europe, Kazakhstan is an important node on Xi’s Belt and Road Initiative and a major international transit hub
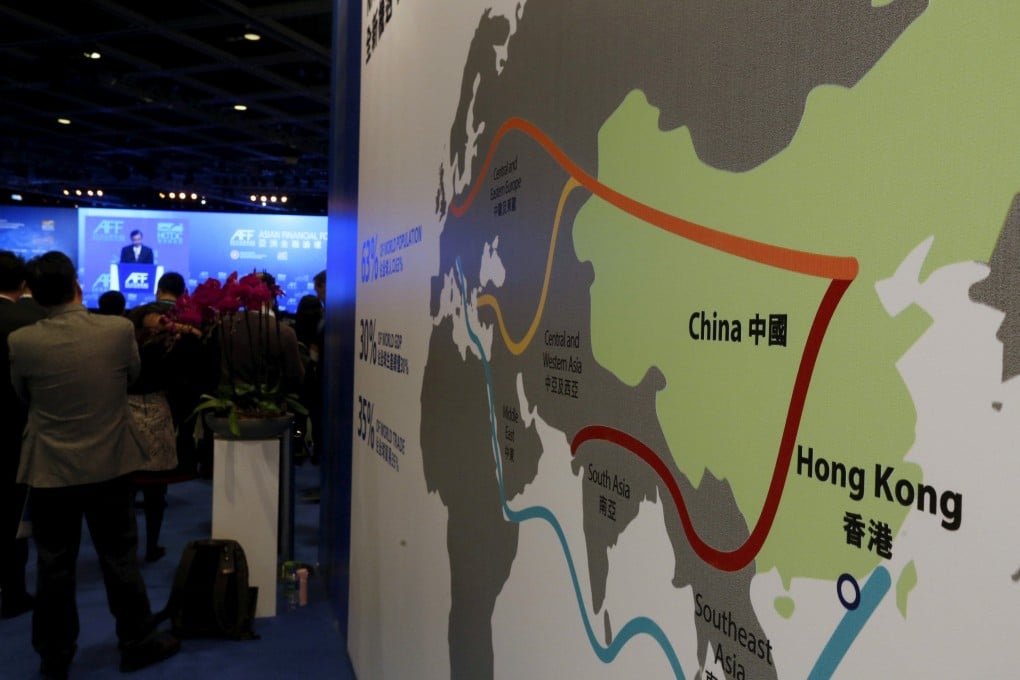
Strategically located between China and Europe, Kazakhstan is an important cross-continental transit route, rich in mineral and oil reserves. Given its geographic position, President Xi Jinping chose to launch the Belt and Road Initiative there in 2013, setting in motion a new era of economic ties between the neighbours.
The Chinese president will meet his Kazakh counterpart Kassym-Jomart Tokayev for talks the host government said were “aimed at further deepening the eternal comprehensive strategic partnership and developing political, trade, economic, cultural and humanitarian cooperation”.
Xi’s visit could be followed by a trip to Uzbekistan to attend the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation summit, though that has not yet been confirmed by Beijing.
How are relations between China and Kazakhstan?
Sharing a border of more than 1,700km with Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region, Kazakhstan is one of China’s most important neighbours.