Three fatal fashion trends in history and why fast fashion may be the worst of all
From mercury poisoning in Victorian hatters to the hot trend for radium beauty products, fashion has unwittingly caused an array of health hazards. But are we going to top them all with the microplastics in fast-fashion items?
October 6 is Mad Hatter Day, a day devoted to the Alice in Wonderland fairy tale crackpot because his top hat bears the label: “In this style 10/6”.
The Hatter’s legendary lunacy raises questions about whether Alice in Wonderland author Lewis Carroll was referencing poisoning caused by mercury in hat production at the time – a popular theory that may stretch the truth.
“People are extremely fond of theories that ‘explain’ the Alice books by connecting things in them to real-life people and events,” says Stephanie Lovett, president of the Lewis Carroll Society of North America.
How hidden toxins in your tattoos can migrate to your lymph nodes
But the mercury connection has been strengthened by actor Johnny Depp, who played the Mad Hatter in the recent Alice in Wonderland films. Speaking to the LA Times in 2009, Depp noted a line where the Hatter says he is investigating things starting with the letter “M”.
“I did a little research and you start thinking about the letter ‘M’ and hatters and the term ‘Mad as a hatter’ and ‘mercury’,” said Depp, whose on-screen hair evokes the metal’s ability to dye things orange.
Certainly, real hatters suffered from mercury-triggered tics, convulsions and delirium. The brain disorder was so rife in their ranks that it became known as “hatter’s shakes”.
An ever-flowing fountain of youth and beauty has at last been found in the energy rays of radium
But other period fashion items could be just as harmful. One deadly threat stemmed from the colour green, which despite its soothing visual effect had toxic roots. Green dresses, wallpaper and more were dyed with pigment containing arsenic, an extremely harmful chemical element.
“People knew of arsenic as a poison, yet it was persistently used for dying clothing and hair accessories, as well as being used in wallpaper, furnishing fabrics and even used as a food colouring!” says analyst Lucinda Hawksley, the author of Bitten by Witch Fever: Wallpaper & Arsenic in the Victorian Home. “The reason people loved it was because it created such a gorgeous vivid green colour.”

Manufacturers knew full well that the arsenic involved in producing the lovely colour did harm, Hawksley adds, but they ignored its impact because they cared little for factory workers’ welfare.
The book Fashion Victims: The Dangers of Dress Past and Present recounts how, in 1861, a 19-year-old artificial flower maker called Matilda Scheurer, whose job involved dusting flowers with green, arsenic-laced powder, suffered horribly.
Scheurer convulsed, vomited and foamed at the mouth. Like her bile, her fingernails and the whites of her eyes were green. Before she died, she even saw green. Later, arsenic was identified in her stomach, liver and lungs.
Horrific suffering could also be caused by a later hot fashion trend based on another dreadful metallic substance: radium.
Residual traces of the early 20th-century craze for the radioactive metal can be found at the Curie Museum in Paris. Named after pioneering radioactivity researcher Marie Curie, the museum features a line of cosmetics called Tho-Radia.

The Tho-Radia line included skin cream, powder, cleansing milk, lipstick, even toothpaste: all laced with radium. “No pretty smile without pretty teeth,” said the Tho-Radia toothpaste puff that trumpeted a delicious sensation of freshness.
The lethal line that promised youthful beauty was endorsed by the mysterious Dr. Alfred Curie. No relation to Marie, Alfred probably had about as much nous as Carroll’s Cheshire Cat. In fact, the quack may have never even existed, but his outward medical clout must have reassured clients keen to have a healthy glow.
Equally dubious radium beauty products could be had in Germany and England. London-based Radior peddled a line of radium-laced products including rouge, talcum powder and vanishing cream. “An ever-flowing fountain of youth and beauty has at last been found in the energy rays of radium,” Radior’s advertising said.
Toxins appear to stay in fashion for labels snubbing Greenpeace campaign
Other manufacturers exploiting the atomic-age craze offered radioactive watches, butter, chocolate and even condoms “sold for protection against disease”.
At special spas, beauty seekers could laze in lovely radium mud, rinse with radium water then, after applying radium cream, walk away soft and glowing, if sick. Anyone exposed to high radium levels may experience ills including fractured teeth, cancer and death, says the Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
Even now, the fashion industry is dogged by toxins. The environmental group Greenpeace lists 11 dodgy chemicals with a modern fashion footprint – including mercury, which still occurs in some dyes – and runs a clean-up campaign called Detox My Fashion. Together with the actions of over half a million designers, bloggers, fashion fans and activists, 20 global fashion brands, including Adidas and Zara, have committed to detoxing their clothes, according to the campaign website.
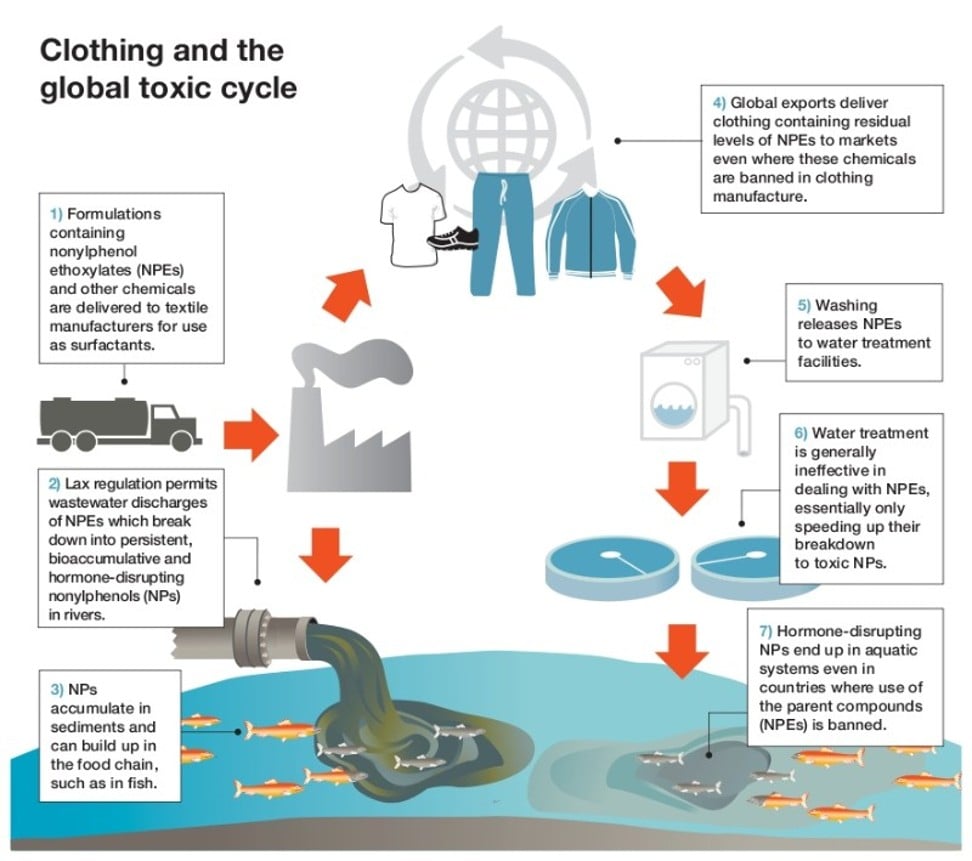
Lu Yen Roloff, communications lead for the campaign, says that some countries, including China, are raising the bar for chemical management. “However, the rising volume of clothes produced in the fast-fashion system leads to new and larger problems.”
Sixty per cent of new clothes, she explains, are made from cheap polyester and other synthetics. The materials cause a new kind of pollution – microplastic fibres that enter the water system, and even tap water.
“We don’t even know yet how this affects our health,” Roloff says. “But it is deeply worrying that we throw out so many clothes that are not biodegradable and which end up in the food chain.”
Four products to protect your skin from Hong Kong’s air pollution
It seems our addiction to dubious fashion-related substances may not be over just yet.
