Chinese coronavirus patient recovers after more than 100 days on controversial life support machine
- The patient from Guangzhou spent almost twice as long hooked up to an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation machine as other survivors
- Some critics have questioned the ethics of using the treatment because of the cost and high death rates
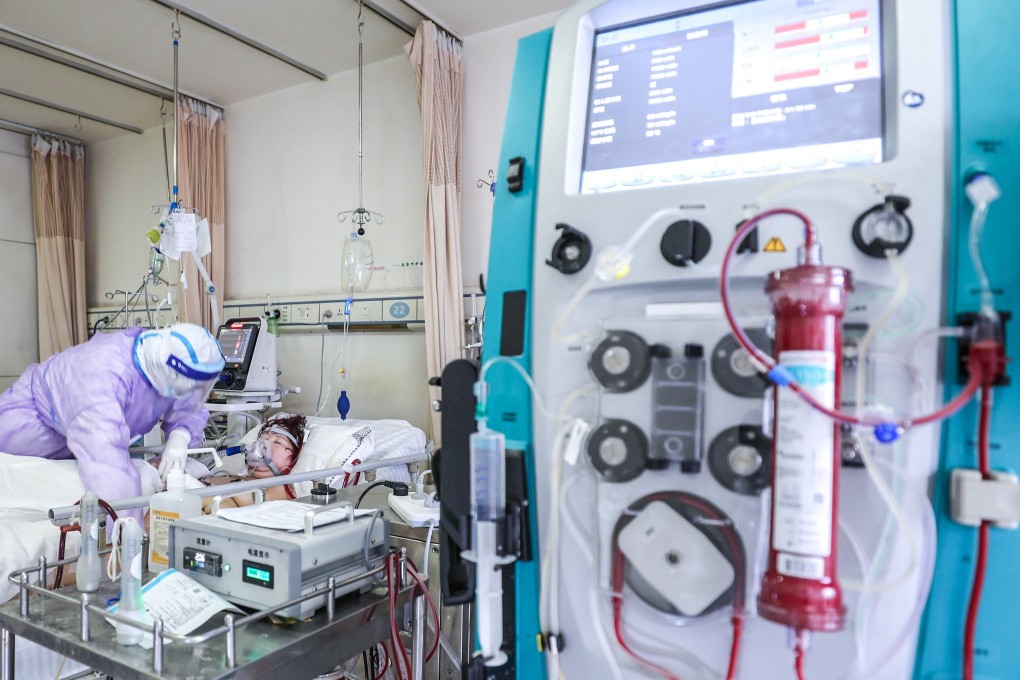
The treatment was pioneered in the 1970s to treat babies in intensive care, but its use on adults has proved controversial, both because of the cost and concerns that it prolonged the suffering of patients who eventually died.

03:49
World’s first coronavirus reinfection case confirmed in Hong Kong, a university study reports
The patient, who was seriously obese, was admitted to hospital in early February with breathing difficulties and was showing signs of heart failure.
The ECMO machine functions as an artificial lung and heart and drains blood out of the body, enriches it with oxygen and pumps it back. After being originally used to keep babies on life support it has been increasingly used worldwide to keep seriously ill adults alive.
But Covid-19 makes it particularly hard to treat patients because serious inflammations increase the risk of uncontrollable bleeding, which cannot be treated with drugs because of the risk of clotting the ECMO’s oxygen exchange membrane.