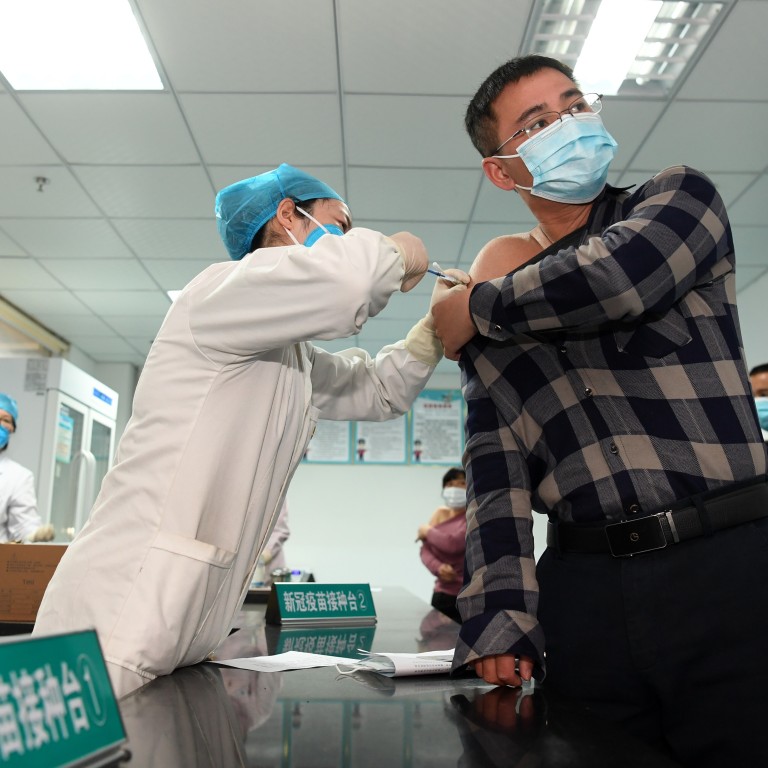

Coronavirus: a flurry of international orders for Chinese vaccines
- At least 10 countries have signed up for the shots from Sinopharm and other providers
- It’s an opportunity for Beijing to burnish its global reputation but it all depends on transparency, observers say
The approval is a milestone for Beijing, which has played up its plans to make its vaccines a “global public good” and could make a big difference to the very limited supplies, according to analysts.
At least 10 countries in Latin America, the Middle East and Asia have signed up for doses from China’s vaccine developers, which also include Sinovac Biotech and CanSino Biologics.

01:35
China approves first domestically developed Covid-19 vaccine
Pakistan joined that list with an announcement on Thursday, saying it planned to buy 1.2 million doses from the company. The two-dose jabs, enough to cover 600,000 people, are the country’s first official confirmation of a vaccine purchase.
Hungary also expressed interest in Covid-19 vaccines from China, with a senior official saying the country planned to rely on shots obtained directly from China or through a European Union procurement mechanism.
A day earlier Ukraine signed a contract to buy 1.8 million doses from Sinovac. The company has yet to announce results of its global trials, but, like Sinopharm, was granted emergency use authorisation in China in July.
Observers said that by supplying vaccines to the rest of the world, China had a chance to bolster its international reputation and partnerships.
Drew Thompson, a visiting senior research fellow at the Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy at the National University of Singapore, said supplying vaccines was “an important benchmark for China in terms of its status”.
As China doles out coronavirus vaccine in Southeast Asia, US withers in a leadership vacuum
“It’s definitely a point of prestige for China to have vaccines, not just for its domestic needs, but to provide abroad, just like the major US pharmaceutical companies and Russia pharmaceutical companies,” Thompson said.
Dominic Meagher, a visiting fellow at the Australian National University, agreed that it would be a “win for China” and global public health if China could successfully roll out Chinese vaccines.
But it was a highly complex task and it was not clear how it would play out, he said.
“Until people are actually vaccinated safely and effectively, it’s a promise,” said Meagher, who is researching China’s response to Covid-19.

01:50
China’s Sinovac Covid-19 vaccine proves more than 50 per cent effective in Brazil trials
Egypt is also among countries to already receive doses of the Sinopharm vaccine. Its health ministry signed a letter of intent for Covid-19 vaccine cooperation with China on Thursday, according to the Chinese embassy in Cairo.
Along with Morocco, Egypt is expected to be a production centre for Covid-19 distribution in Africa.
One of the Sinopharm vaccine’s advantages is that it can be stored and transported at normal fridge temperatures. If competitively priced, the vaccine could be a “game changer” in the sector, according to global health governance researcher Sara Davies.
“It’s got all the bells and whistles to be a big deal, but we just need more information. It’s really important if China wants to claim leadership [in global vaccine supply] and reach a bigger market, they are going to have to start coming forward with a lot more information,” said Davies, a professor at Griffith University in Australia.
But officials have released very little information about the analysis of the vaccine, saying only that trials included 60,000 people in several countries, mild fever occurred in less than 0.1 per cent of the participants and there was a serious allergic reaction in about two per million.
Coronavirus: people in China ‘the most willing among 15 countries to take a vaccine’
An executive from Sinopharm subsidiary China National Biotec Group, which is responsible for developing the vaccine, said more details would be released and published in scientific journals.
The vaccine has yet to be endorsed by the World Health Organization, a gold standard for domestic regulators and UN agencies placing vaccine orders.
On Thursday, the WHO gave its first emergency use validation for a Covid-19 vaccine to Pfizer-BioNTech.
That might be the next hurdle for the Sinopharm vaccine, according to Davies.
“It’s one thing to be able to get countries signing on. It’s another to say you are a leader – to do that there has to be transparency and that international seal of approval,” she said.
Additional reporting by Reuters

