Target asymptomatic Covid-19 cases to stop community spread: Chinese study
- People who test positive but show no sign of illness need to be isolated too, Peking University researchers say
- Screening and quarantine on arrival at airports needed to tackle high percentage of asymptomatic infections among travellers
“Screening for asymptomatic infection is required, especially for countries and regions that have successfully controlled Sars-CoV-2,” the team said, referring to the official name for the coronavirus that causes Covid-19.
“Asymptomatic infections should be under management similar to that for confirmed infections, including isolating and contact tracing.”
The scientists based their assessment on the findings of 95 studies published between January 2020 and February this year covering nearly 30 million people who had undergone Covid-19 tests.
The results were published in the peer-reviewed Journal of the American Medical Association Network Open on Wednesday.
The studies were mostly from Europe, North America and Asia.
According to the World Health Organization, a person infected with the coronavirus might not experience any symptoms and can transmit the virus to others without knowing.
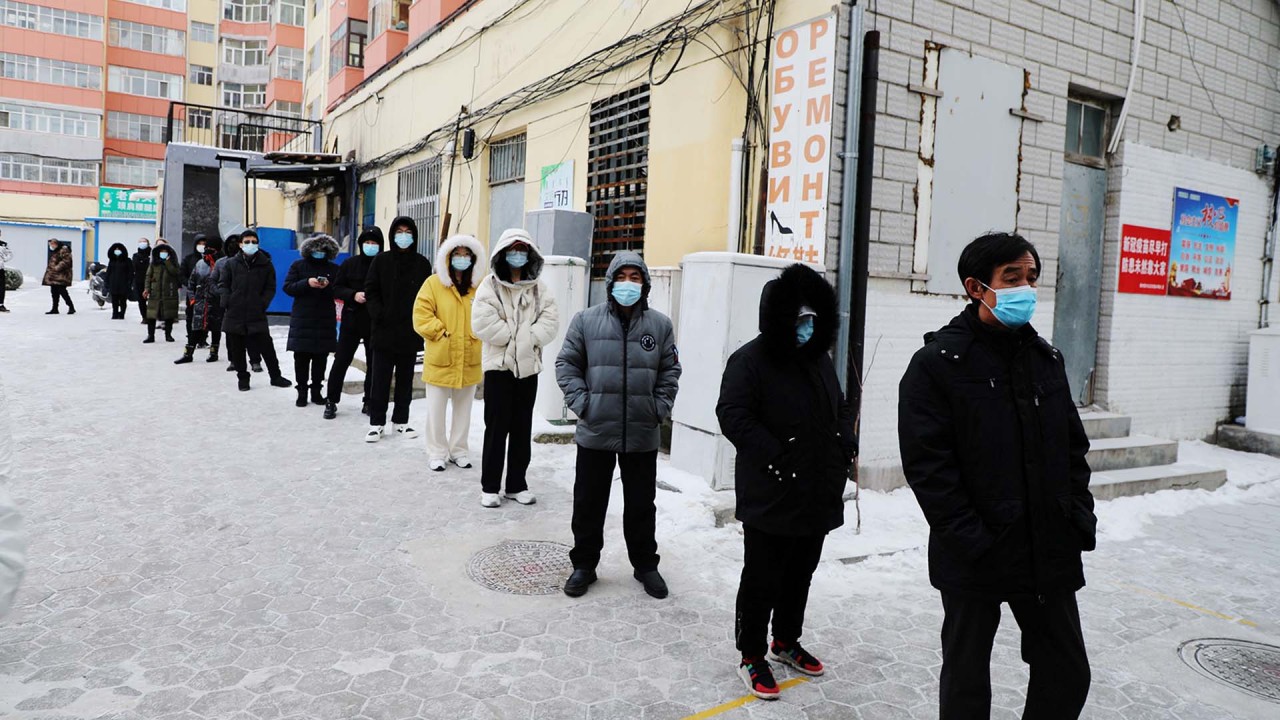
The Peking University team found around 40 per cent of “community residents” who had Covid-19 were asymptomatic, raising the need for the general population to be tested.
“To prevent further transmission in communities, asymptomatic individuals among the general population should be tested. If resources are limited, workers in specific industries such as air transportation should be routinely tested,” the scientists said.
The study also found only 0.25 per cent of the people tested had asymptomatic infections.
They cited a study that documented the post-lockdown testing of nearly 10 million residents of the central Chinese city of Wuhan, the first epicentre of Covid-19. The mass testing in May 2020 uncovered 300 asymptomatic cases and no new symptomatic infections.
China has used mass testing, frequent contact tracing, lengthy quarantines and strict border controls to control the spread of the virus. The northern Chinese border city of Manzhouli, for example, has conducted 14 rounds of daily citywide testing during its ongoing outbreak, uncovering more than 500 Covid-19 infections.
The country’s “dynamic zero-Covid strategy” aims to control outbreaks as quickly as possible through mass testing and restrictions on movement and transport. But infections are still breaking out in the country in waves, some caused by cases seeping in from border regions.
According to the Peking University analysis, asymptomatic cases were also a higher share than average among the pregnant women, air or cruise ship travellers and nursing home residents or staff with confirmed infections.
The team found around 53 per cent of infections among air or cruise travellers were asymptomatic.
“This finding of a high percentage of asymptomatic infections among air or cruise travellers suggests that screening and quarantine on airport arrival is important for reducing community transmissions, especially in countries without local transmission,” the team said.
As for health care workers or in-hospital patients, about one-third of people who had Covid-19 were asymptomatic, the researchers found.
“Because asymptomatic health care workers might contribute to disease spread in and out of hospitals, surveillance of asymptomatic individuals is important for infection control and transmission reduction in health care settings and community,” they said.