Advertisement
China prepares to launch space station module for science experiments
- The Tiangong space station’s second component is expected to take off on Sunday afternoon, though Chinese space authorities have yet to confirm
- The new module, named Wentian, will support research on how microgravity and space radiation affect cell, plant and animal growth
Reading Time:2 minutes
Why you can trust SCMP
6

China is expected to launch the second component of its Tiangong space station on Sunday, carrying new gadgets, robotic arms and equipment for experiments on the effects of space on plants and animals.
The Wentian experiment module, weighing 20 tonnes (22 tons), is currently packed inside a Long March 5B heavy-lift rocket and sitting on a launch pad at the Wenchang Space Launch Site in the southern province of Hainan.
The launch is expected to take place at 2.20pm Beijing time on Sunday, though the China Manned Space Agency has not confirmed it yet, only saying that various tests are now under way to prepare for the mission.
Wentian is equipped with several experiment cabinets, each designed as a “miniature laboratory” to host a series of experiments over the next 10 years, said Wang Ke of the Chinese Academy of Sciences during an online talk last month.
Advertisement
The refrigerator-sized cabinets will support life sciences research on how microgravity and space radiation affect cell cultivation and the growth of plants, insects, small mammals and microbes, according to a space station handbook.
The experiment module will allow the Chinese space station to support over 1,000 scientific experiments during its lifetime, said Wang, who is a senior member of the cabinet development team.
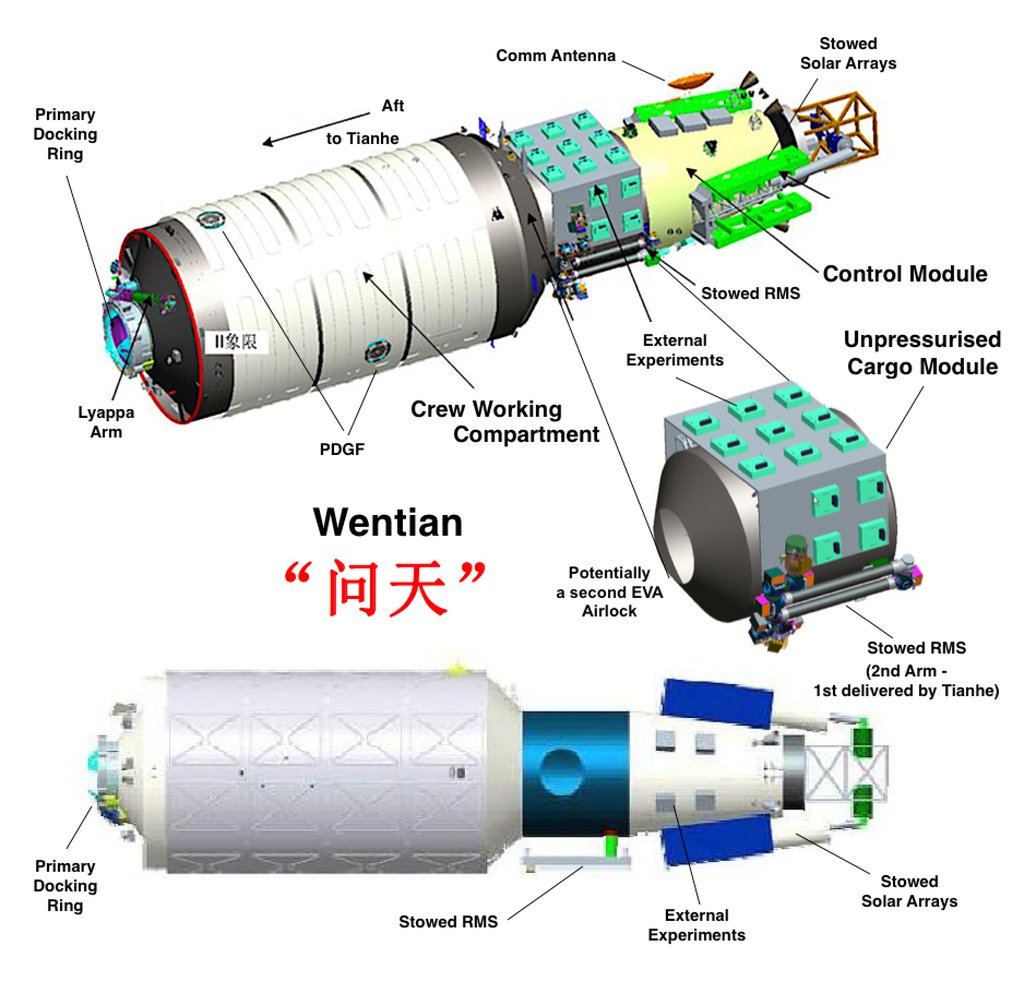
After Wentian enters orbit, it will first rendezvous with Tiangong, now under construction in low-Earth orbit, from the forward docking port of the core module. A 10-metre (33-foot) robotic arm on the core module will then grab Wentian, rotate it 90 degrees and move it to another docking port.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Select Voice
Select Speed
1.00x