How can businesses establish first-mover advantage in metaverse?

[Sponsored Article]
Asia's leading tech firms, luxury brands, fast-moving consumer goods companies and high-end manufacturers are actively exploring the opportunities of extending their online presence to the metaverse. Metaverse platforms, meanwhile, are testing the market for virtual real estate, according to recent research by EY-Parthenon, EY's consulting arm.
The word 'metaverse' has become the most talked-about buzzword since the start of 2022. It is often used as a synonym for virtual reality, and the term was first coined by Neal Stephenson in his 1992 sci-fi novel Snowcrash. The emergence of this whole new virtual space is reminiscent of what it was like in the dot-com era when leading businesses were swift to establish a presence and drive customer engagement.
To make the most of the metaverse, businesses should set a clear strategic vision, execute it efficiently, and keep iterating on their strategy once it is set in motion, says Ben Kwan, Ernst & Young Parthenon Strategy and Transactions Partner and Head of Digital Innovation. "To capture the first-mover advantage, businesses must embrace an innovative mentality, and be open to collaboration with and investing in start-ups."
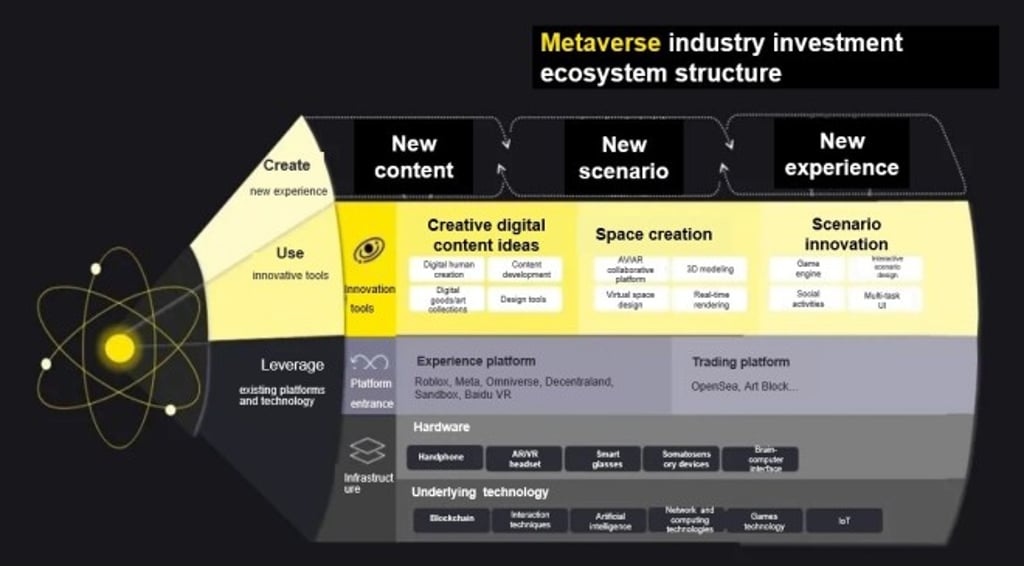
Understanding the metaverse ecosystem
According to EY-Parthenon, the metaverse ecosystem can be broken down into the infrastructure, platform and application levels. The metaverse infrastructure comprises network providers, programming standards, and hardware devices.
Some metaverse platforms, like the Roblox gaming platform and Horizon Worlds by tech giant Meta (Facebook), as well as the decentralised Decentraland and Sandbox, can be experienced by just using a laptop or smartphone, but to best experience these platforms and ultimately all metaverse platforms, a VR headset is the best entry point. Trading platforms are currently geared towards trading non-fungible token (NFT) assets.
On the application level, the metaverse platform must support a variety of applications for content, scenarios and experiences across all devices and cater to a large pool of users concurrently.
Metaverse ecosystem participants
The metaverse supply chain can be broadly classified as underlying technology providers, hardware suppliers and innovative start-ups. Underlying technology providers have a mastery of blockchain, interaction technologies, artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies.
End-user devices include smart phones and handhelds, AR/VR headsets and glasses, while their manufacturers, partially or wholly owned by tech giants, are rushing to enter the metaverse supply chain. A new breed of metaverse start-ups, scale-ups and unicorns are developing their ‘web3’ ideas in content, social, gaming and software into viable businesses for the metaverse.
Unprecedented level of collaboration
If the metaverse becomes secure and stable enough, it will allow for cost reduction and efficiency improvement in communication. It could also be applied to decision-making, teaching and training, and medical diagnosis, among countless other potential use cases.
Leveraging extended reality (XR), mixed reality (MR) and augmented reality (AR), the metaverse allows people to see, hear and interact with others in a virtual setting while seeing others’ facial expressions and expressing emotions. These immersive features offer an unprecedented level of collaboration, virtual co-creation of content, and content sharing via new forms of connectivity, such as holograms.
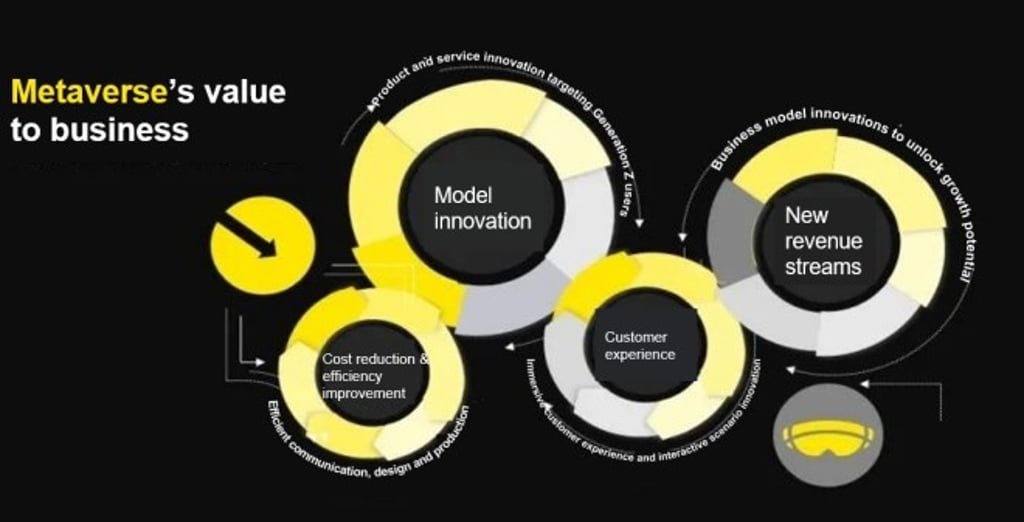
Exploring new revenue streams
A metaverse product is a digital product that exists in the same space as other virtual objects. Many retailers and luxury brands are starting to create virtual digital products on metaverse platforms as they explore new revenue streams.
Although the metaverse retail space is still in the early stages of experimentation, the market has warmly welcomed it. Meanwhile, businesses are seeing growth in the Gen Z market, and a wide variety of companies are trying to attract this demographic in the metaverse.
This emerging retail market has led to more companies investing in virtual experiences and brand spaces, from virtual exhibitions and avatar streaming to virtual theme parks. Metaverse also brings the interest in a gamified experience mainstream. For example, a luxury brand has partnered with digital artist Beeple to launch a mobile game. The digital art collection of the artist is embedded into the game.
“Businesses need to understand how the metaverse works and get a digital business strategy to fully take advantage of all that metaverse offers,” says Kwan. “They should experiment with pilot projects to find a business model that works for them and innovative ways to engage with their customers in the metaverse. At the same time, it is important that enterprises invest in and support the growth of metaverse start-ups.”
“With the emergence of the metaverse, there are many opportunities for disruptive business model innovation,” he adds. “The future is full of limitless opportunities for brands to evolve their virtual offerings.”
About EY-Parthenon