University researchers contribute to verified social benefits, RAE 2020 finds
Conducted by the University Grants Committee (UGC), the Research Assessment Exercise (RAE) 2020 clearly identifies that research projects by Hong Kong universities deliver far-reaching positive social impact.

[Sponsored Article]
The UGC recognises the need to incentivise local universities to conduct more research of social relevance with high economic and social benefits and has sought to acknowledge the impact generated by their research. Hence, UGC decided in 2016 to include a new component called “Research Impact” in its RAE 2020. The RAE is aimed to encourage world-class research by UGC-funded universities.
Research impact, as defined by UGC, is “the use of knowledge obtained through research to affect the world beyond academia, such as industry, health, the environment, or the society in general.”
On another level, the impact element provides solid evidence of research’s benefits.
Excellent research impact
For the RAE 2020, UGC-funded universities submitted impact case studies, which were required to show a clear pathway between the initial research and the eventual outcome as well as how the submitting unit had contributed to that outcome. The submissions should also be substantiated with verifiable evidence.
All of the assessed universities have made outstanding achievements in research impact because the ratings awarded show the overwhelmingly high-quality impact demonstrated by the cases, UGC says. Their submissions show how far-reaching and active is the engagement of the universities with the society and the economic developments of Hong Kong and beyond. Among the submissions, 89 percent (306 cases) claimed impact within Hong Kong and 76 percent (261 cases) claimed impact beyond the city.
Meanwhile, many submitted cases were based on multidisciplinary research and collaborations with the trade and industry, allowing the impact to reach different aspects of life and segments in the society. Collectively the case studies demonstrate the sheer energy and commitment channelled into the outreach into schools, the community and society, particularly the underprivileged. The case studies can be accessed via the following link:
Four exemplary and pioneering impact case studies submitted to the RAE 2020 demonstrate how research brings benefits to society.
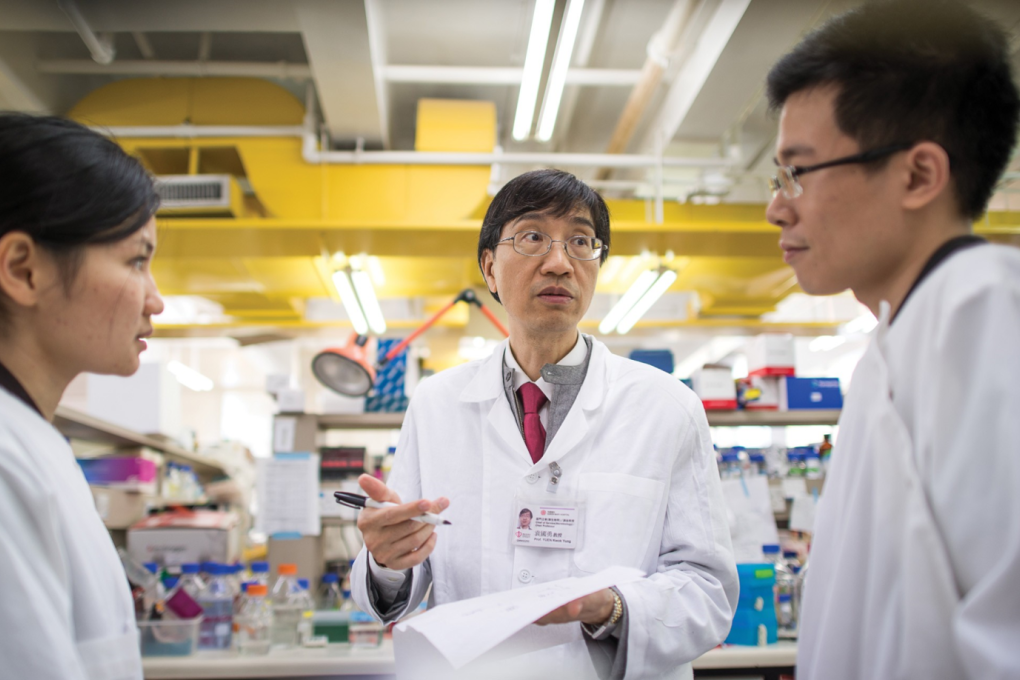
Health Sciences: Discovery of novel coronaviruses (CoV) with public health significance
During the SARS epidemic in 2002-03, researchers at a university in Hong Kong were the first in the world to discover SARS-CoV-1 and developed rapid diagnostic tests. They also discovered its ancestral virus, the bat SARS-related CoVs in Chinese horseshoe bats, which subsequently turn out to be ancestrally related to SARS-CoV-2 of 2019. Their efforts have global health and economic impacts in four areas:
- Commerce and industry: Numerous rapid diagnostic kits have been developed by companies around the world based on the Hong Kong research team’s results.
- Healthcare services and patient benefits: Antiviral treatments and diagnostic kits developed based on this research are in use in hospitals across the globe.
- Health policies: the tracking of SARS origin in animals provided crucial guidance to public health measures internationally in segregating the animal carriers from humans, introducing continuous surveillance of animal viruses, and identifying potential emerging zoonotic viruses.
- Education: The team members have actively played a wide range of advisory roles, with direct influence on international and local protocols for promoting personal and environmental hygiene and good travel advice.
Engineering: Motion capture and assistive systems
This mechanical engineering case study centred on the innovative combination of technologies developed by an engineering department. They include a smart, magnetorheological actuator for assistive knee braces and robotic exoskeletons developed for people with mobility problems. Meanwhile, the department developed a novel method for real-time and convenient modelling and evaluation of human gait to support rehabilitation. A fuzzy expert system was developed by combining the innovations with positive impact on:
- Patient rehabilitation: The system assists gait rehabilitation by taking the patient’s physical condition and gait analysis results as inputs, and deriving suitable levels of different assistive functions of the knee braces.
- Technology commercialisation: A startup was established in 2012 which employs more than 300 staff for its operations in China and the USA, working on an affordable, adaptable and versatile motion capture system.
- Sports training: The system is used for training golfers, including over 60 percent of USA PGA top 100 coaches.
- Space programme: A scalable commercial VR version of the system, developed for multi-users with physical props and motion capture, has been used in NASA’s Moon Landing 50th anniversary commemoration.
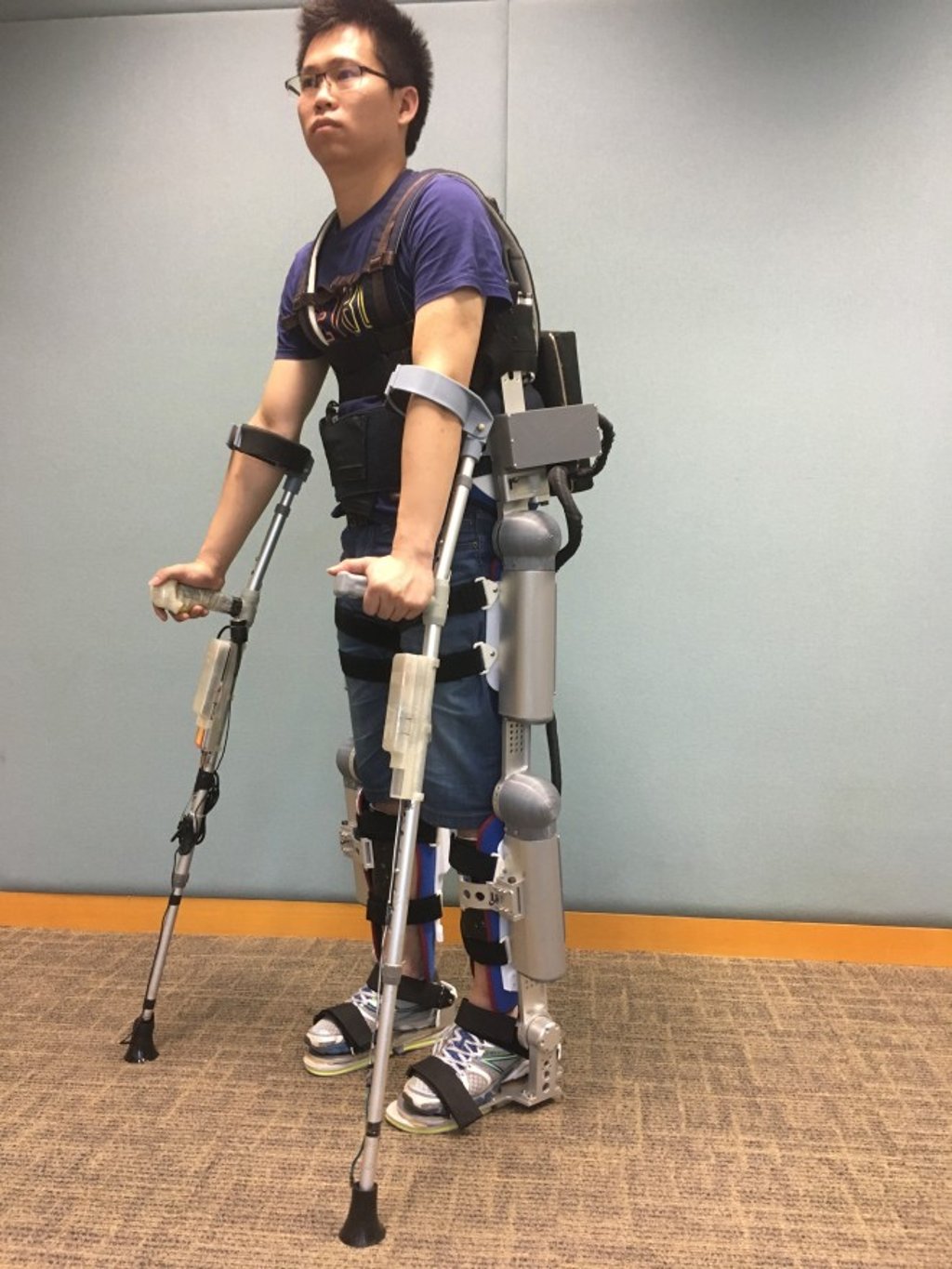
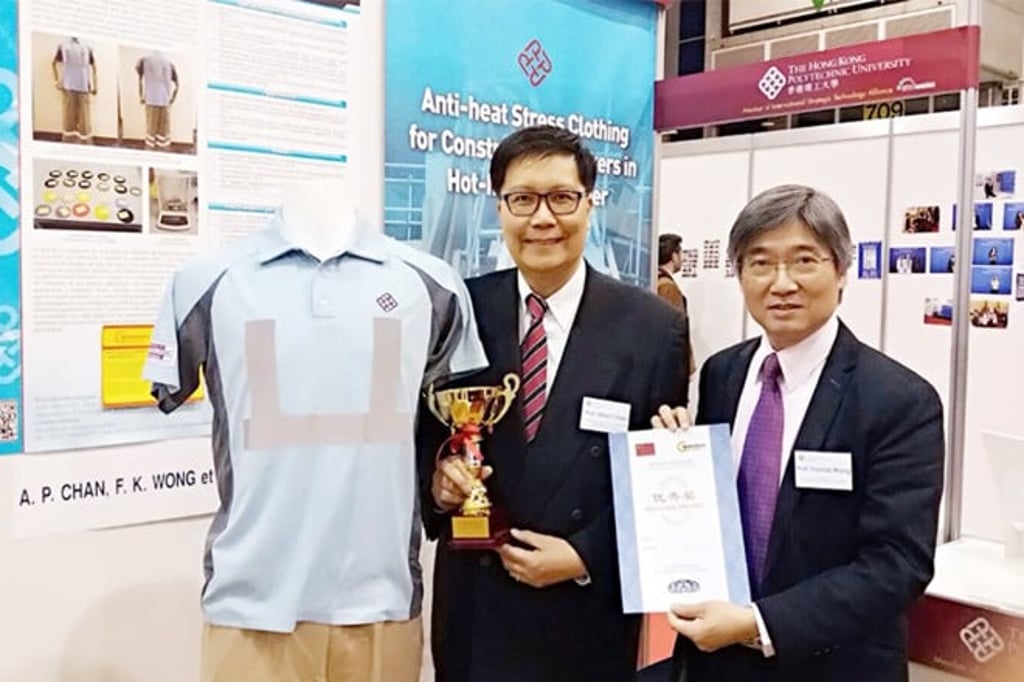
Built Environment: Enhancing construction workers’ health and safety in hot weather
A multi-disciplinary team from the submitting unit, together with partners from local and overseas universities, pioneered a series of heat stress research projects since 2010. The goal was to address industrial heat stress issues. The work involved evaluation of fabric types coupled with developmental work on fabrics and ergonomic design; and a novel approach to occupational intervention research which moved beyond randomised control trials in laboratory settings. The benefits include:
- Product manufacturing: An affordable anti-heat-stress work uniform was developed. It offers around 29-percent heat storage reduction and more than 14-percent improvement in thermal comfort.
- Construction industry: The uniform was licenced to the Construction Industry Council in 2015 and was specified by the government as standard workwear for all public works contracts in 2018.
- The cleaning, gardening and logistics sector: The garments have been adopted for use by these sectors in Hong Kong, Macau, Cambodia and Saudi Arabia, to promote occupational health.

Social Sciences: Better responses to youths-at-risk
This cross-country research project focused on welfare responses to street youths and restorative approaches to school delinquents. The ‘street youths’ research explored the channels through which they were ‘triadised’ and assimilated gang values. The ‘school delinquency’ research identified a strategy called ‘Restorative Whole School Approach’, based on tolerance and acceptance, combined with appropriate social disapproval of delinquency and mediation tactics. This sociology project delivered impact on:
- Youth and Family Services: The team developed for the Macau Government a youth service blueprint which, after initial trials, was transformed into several programmes. New Integrated Youth and Family Services Centres were established. Social workers and police superintendents were trained to work with police-cautioned youths. About 66,000 service recipients have benefited from the programme.
- School Support Network: A Hong Kong Government-funded social worker supervision project aimed at building a positive discipline-oriented school support network and forging an anti-bullying culture among youths, together with development of practitioners’ guidelines and tools. The project benefited nearly 15,000 students, over 2,000 parents and about 3,000 teachers.
- Community Support: In Guangzhou in 2019, training was provided to 200 outreach workers and advice was given to the authorities to consolidate an at-risk youth service model that benefited nearly 20,000 young people. In Singapore, the government received advice on the development of an at-risk youth service model. Forty outreach workers received training on youth gang work and 200 youths received assistance.
