
Migrant workers helped build China’s economic miracle, now they are dying because of it
- They laid the foundations for Shenzhen’s skyscrapers, and its prosperity, and became wealthy in the process. But the labourers from Hunan paid a deadly price
- They didn’t know they had risked their health. Now, as the effects of construction dust take hold, the men are mobilising to hold those responsible to account
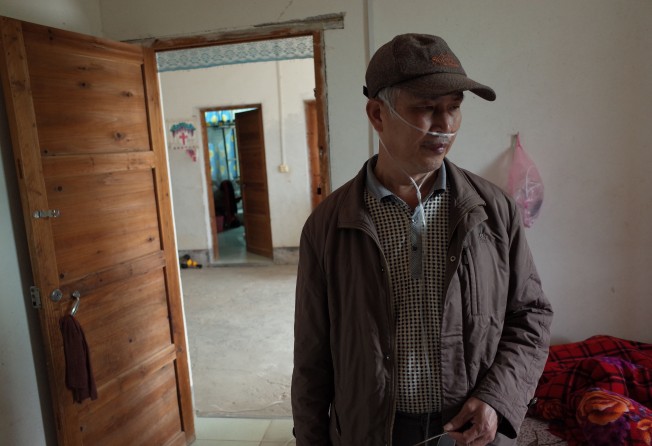

Ill and defeated, Xu Chunlin approached the railing, the limits of a search for justice.
Before him was a nine-metre plunge into Shenzhen’s rush-hour traffic. Behind him stood police he had just clashed with. On the overpass with him were about 80 other former construction workers considering the same desperate calculus.
Leap now? Or wait to die when their lungs gave out?
The journey that led them to that bridge began in the early 1990s. The men were young and healthy then, wide-eyed migrant labourers from rural Hunan province. Shenzhen was a scruffy border boomtown to the south – not yet today’s cosmopolitan hub of 12 million people – where they flocked for off-the-books jobs as drillers.
Many Hunanese worked for years, even decades, boring into the bedrock to build subway lines and the foundations of Shenzhen’s cityscape. But they didn’t know the inadequacy of the US$1.50 cotton masks they were given, or the irreversible harm of inhaling silica dust that caked their faces once their drills bit into granite-streaked crust.
More than 100 labourers from Hunan have died in the past decade from silicosis, an incurable condition caused by inhaled dust particles that scar and harden the lungs.
About 600 more are suffering or slowly dying, the leaders of worker groups say. Three dirt-poor Hunan communities that once survived off their earnings – even saw progress – are now mired in debt and grief while survivors spend their few savings and energy to clamour for compensation.
The lives of these drillers trace diverging realities.
One story is reflected in the gleaming skylines they built: the backdrop for a prosperous middle class of 400 million people who live in China’s cities and power its economy. Another story is framed by struggle: a vast, rural underclass still toils in hazardous conditions, lacking documentation or means to seek redress except through confrontation with the government.
Forty years after China shifted away from its socialist system – and the promise of cradle-to-grave care for workers – the country is settling hard questions accumulated in the rush to modernity.
Who benefited and who suffered? Who is owed compensation and who should pay up?

Since early 2018, Hunan’s ailing drillers, led by Xu and others, have travelled more than a dozen times to Shenzhen to demand help. In early November 2018, hundreds of them occupied a government complex before police dispersed them with batons and pepper spray – further aggravating their weak lungs.
It was during that stand-off – according to the accounts of four protesters, activists and news reports – that workers cornered by police on an overpass threatened to die in a mass suicide by hurling themselves onto an eight-lane road.
Xu, one of the protest leaders that night, says he was ready to die for the cause.
But he also feels responsible for these men, he later explains. He was one of the first Hunanese to bring fellow villagers to Shenzhen in the 1990s, setting off a chain of success and tragedy that would unspool over a quarter of a century.
Standing on that overpass, Xu says, he yelled at the men to back away from the ledge and the madness. Keep calm, he told them, and fight another day.
“China is like a cart. It won’t move forward if you don’t push,” he later says. “If you’re not afraid of dying, you can accomplish anything in this country.”

Steep sandstone ravines carve across Sangzhi county, a part of Hunan province with little industry or even agriculture. But multistorey homes with faux-European balustrades line county road 420. They are the rewards of labouring in cities such as Shenzhen – and monuments to the human cost.
“Everyone builds a big house and then there’s no one to live in it,” says Gu Zhongping, a former driller, as he drives along, pointing out homes of former Shenzhen workers dying or dead.
Gu Hejian, in a house decorated with red posters for his son’s wedding, doesn’t expect to live much longer. Zhong Yichuan, who lived behind a corner store, died two years ago. Wang Zhaogang died in April and was buried by 10 unwell workers counting the days themselves.
More than 26 former drillers in Sangzhi county have died of lung disease since 2009, according to residents, who say deaths are accelerating, with about 100 others who are seriously ill. In two other Hunan counties, Leiyang and Miluo, about 500 villagers who worked in Shenzhen have been diagnosed, according to workers’ representatives.
Although official figures are unavailable, a Hunan city-level document supports the claims. A 2017 health check shows that 290 villagers, mostly in Sangzhi, had silicosis.
Work-related lung diseases have held steady or declined in developed countries as jobs such as coal mining waned and safety standards rose. In China, cases are proliferating.
In 2018, about 873,000 Chinese workers had pneumoconiosis, a broad class of lung disease, up from about 559,000 in 2000, according to China’s National Health Commission. Love Save Pneumoconiosis, a Beijing non-profit, estimates the true number to be much higher – possibly 6 million.
Officials, who are drawing up plans to study the crisis, say 23 million workers are at risk of getting the disease. That’s far more than the 11.5 million at-risk workers in India, 2 million in the United States and 1.7 million in Europe estimated by health authorities and researchers.
Workers who inhale dust and tiny mineral crystals found in rock and sand do not immediately feel symptoms. But over months, sometimes decades, the lodged particles do devastating damage.
Walking, even talking, becomes difficult. Lying flat creates the sensation of suffocation, so most patients sleep sitting next to a small oxygen machine. In the latter stages, they suffer heavy wheezing, steep weight loss, frequent bouts of colds and fevers. Pneumonia and tuberculosis can easily turn fatal. Sooner or later, the lungs simply give out.
Behind a rubbish-strewn basketball court that serves as a village square in Sangzhi county, a country doctor, Li Li, watches as Cheng Xiangyong, a 49-year-old who is doubled over the couch in her office, coughs up long, thick goop.
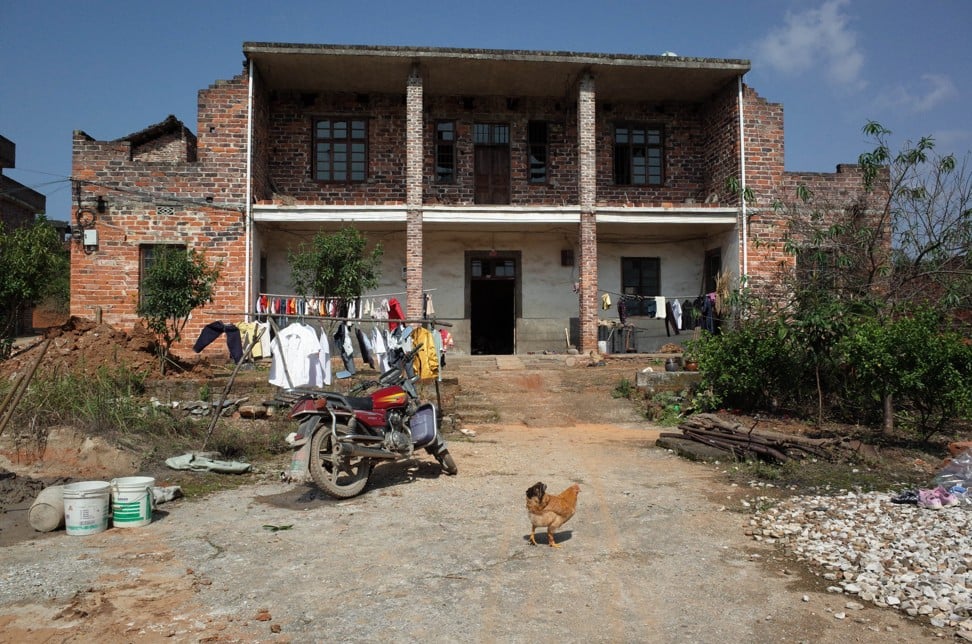

“He should have 1½ to three years to live,” Li predicts as she prepares familiar drips: ambroxol to dissolve mucus, aminophylline to dilate air passages and an antibiotic.
Three of her silicosis patients have recently died. Sick workers keep streaming in. The one-room clinic she converted out of a ramshackle storefront doesn’t have proper medicine, equipment or, Li admits, know-how.
But for sick workers who need care several times a month, it’s better than a two-hour drive to a city hospital or six hours to the provincial capital, Changsha, she says.
“We have so many people like this,” Li says. “I tell them not to come. I can’t handle them. I can’t handle the risk.”
As he clutches a table, Cheng’s hoarse wheezes fill the room. He had drilled on and off in Shenzhen for 13 years until 2017, when his symptoms surfaced. His weight recently plummeted from 70kg to 51kg.
Cheng worries about dying as quickly as his friend Gu Erhu, whose lungs failed on August 14, just hours after they spoke. Cheng also worries about not having money to buy his own coffin, and about leaving his wife, Chunyue, and his 82-year-old mother to fend for themselves.
“We’ll manage,” Chunyue says, smiling across the table. “There is no other way.”
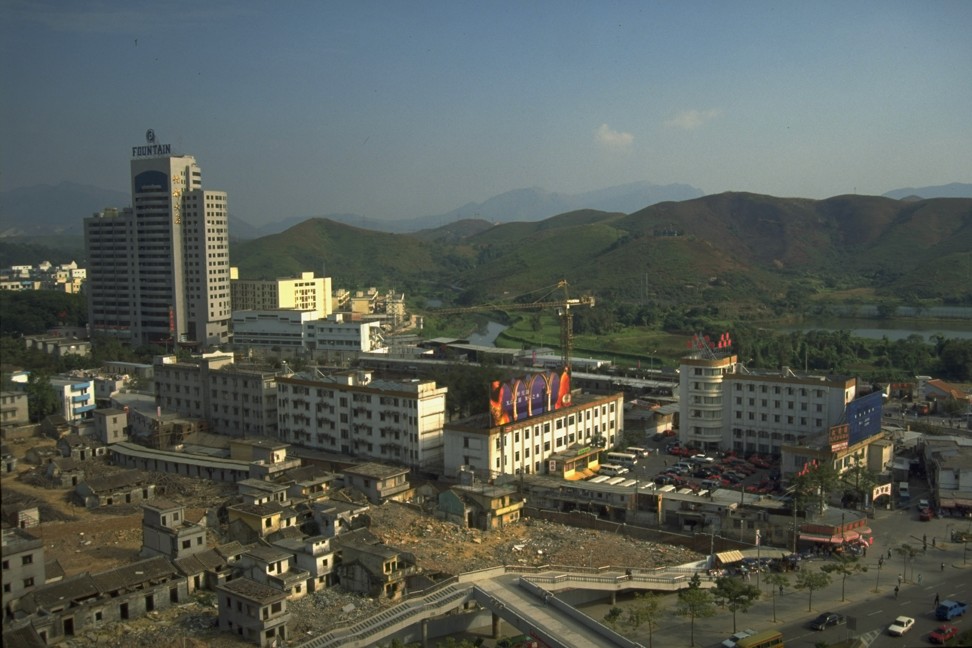

Shenzhen had a population of 30,000 in 1980, when China’s Communist leaders designated it the country’s first free-market laboratory. Within decades, farmland and mangrove swamps would turn into factories for the world’s iPhones, Asia’s fourth-largest stock exchange, and high-rise towers and accommodation for the super-rich such as US$4,000-a-night St Regis hotel suites.
Shenzhen’s economic output soared from US$4 million in 1980 to US$340 billion in 2018. Officials have often marketed the city as China’s window to the world.
For Xu – decades before he thought about jumping from the bridge – Shenzhen was a path out of hardscrabble Leiyang county in Hunan.
A short and badly underfed 21-year-old in 1989, Xu first ventured 800km south that year with four brothers to work at Shenzhen construction sites. He returned for Lunar New Year with 5,000 yuan, he recalls, and immediately spent it all on more than 1,500kg of rice to pile in a granary so his family could recover to their healthy body weights.
Within four years, Xu was working as a middleman. That meant introducing villagers to Shenzhen’s subcontractors, who set aside half the positions at work sites for the Hunanese. Sometimes the jobs were worth US$45,000, making Xu a relatively rich man on his cut.
“Everybody in the village wanted to know me because I had jobs,” he says, sitting in a three-storey brick house he built in Leiyang county. “Every boss in Shenzhen wanted to know me because I had men.”
The Hunanese crews relied on handheld jackhammers and controlled explosives to open the ground, sometimes 45 metres deep. They would then pour concrete into the pits to make pillars that could bear a building’s load.
“Pay attention and be safe,” one Hunan worker, Zhong Pinxie, recalls bosses saying before they threw him onto a site with almost no training. In those early years, he says, he was given a simple conical mask to cover his mouth and nose. He didn’t wear goggles or earplugs before going down a 1.2-metre-wide pit for four-hour shifts.
Zhong worked so many drilling jobs that he learned Shenzhen’s subterranean geography. The new subway line in Luohu bored easily through crumbling rock. In the Nanshan flats, where malls and Shenzhen University rose, it was granite-streaked earth that kicked up thick dust.
“When the drill bit touches,” Zhong says, “it’s like a cannon goes off in your face.”
That’s precisely what would cause the opaque globules that dotted his lungs in X-rays last year – a telltale sign of advanced silicosis. But Zhong didn’t know that at the time; few did. Education and awareness on worker safety was scant, and symptoms of lung disease wouldn’t surface for several years.
Middleman Xu had shifted into administrative work by 2008, when a construction engineer handed him a one-page document about pneumoconiosis and said quietly: “Don’t do this job too long.”
“I thought he must know something,” Xu says. “But from beginning to end, none of the companies or government ever did any publicity about cause or effect.”
By 2009, silicosis was becoming hard to ignore. Media reports surfaced about subterranean drillers falling ill. Groups of workers from Leiyang started petitioning Shenzhen authorities, who agreed to give payments of up to US$15,000 to those who could prove their employment.
But for most drillers, that was impossible.
Since the 80s, when China’s economic reforms unshackled peasants from their land and sent them streaming into cities in search of work, nearly 300 million migrant workers have occupied a legal grey area.
As it embraced free enterprise, the Communist Party neglected workers from the countryside, members of the very class it ostensibly championed.
Despite a 2008 law requiring all employers to offer written contracts, only 35 per cent of migrant workers signed them in 2016 – a number that is falling, according to China’s National Statistics Bureau, which has stopped releasing data. A 2014 nationwide survey by Love Save Pneumoconiosis found that only 7 per cent of workers with the disease reported ever signing a contract.
By the time workers feel progressively worse 10 years later, they can’t identify which company they worked for when they contracted the disease
The construction industry – a sector that accounts for a quarter of all work fatalities – is known for relying on subcontractors called baogongtou who hire workers informally, says Eli Friedman, a China labour expert at Cornell University, in the United States.
The system, he says, “pushes risk to the bottom”.
Work-injury insurance also has lagged. China launched a national plan in 2004. Today, 80 million migrant workers, or roughly 27 per cent, are covered, officials said in May.
Shelly Tse Lap-ah, director of the occupational health studies centre at the Chinese University of Hong Kong, says the Shenzhen workers have been further handicapped by the latent nature of pneumoconiosis.
“By the time workers feel progressively worse 10 years later, they can’t identify which company they worked for when they contracted the disease,” Tse says. “Companies may already be bankrupt.”
With little hope of compensation for workers, grief – and anger – boiled over in rural Hunan last year.
Xu has watched the death toll in his villages tick up to more than 70. Six sick men have committed suicide. Local clans such as the Caos, who have buried three brothers who contracted pneumoconiosis in Shenzhen, are devastated.
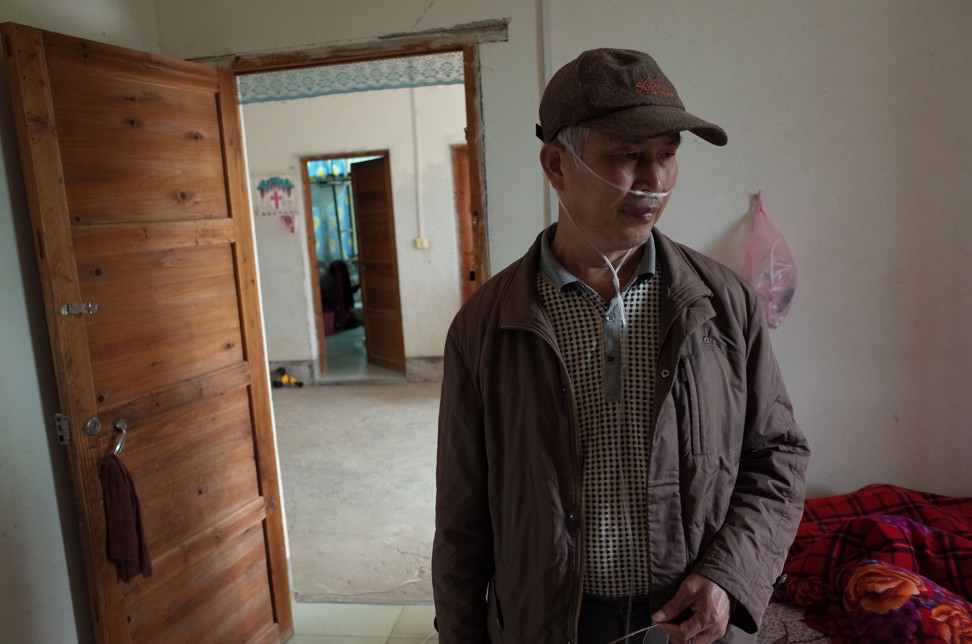

So is Xu’s own family. Four of his brothers, who worked in the Shenzhen pits, have died, the youngest at 26. Xu, himself diagnosed with terminal silicosis, is well off financially, but Leiyang county is struggling.
“We had to do something,” he says. “People need to survive.”
Similar events have been playing out in Hunan’s Sangzhi and Miluo counties, as ill workers mobilise to take their demands to Shenzhen, where they have joined forces.
On November 5, 2018, a large group of workers, furious about a lack of progress, occupied the government compound and demanded to see Shenzhen’s mayor. They slept overnight on mats and by the night of November 7, more than 300 workers had gathered at the scene.
That evening, authorities made their move. Videos of the incident show riot police with pepper-spray guns flushing the protesters out of the government complex. The retired workers keel over on the pavement outside, coughing, as paramedics whisk away the injured.
Dislodged from the building, scores of angry protesters regrouped, then veered toward an overpass, where they threatened to jump, say three petitioners from Leiyang and Sangzhi. It was a final gambit.
It worked.
Police rushed to block the crowd surging onto the bridge. By midnight, city officials had emerged to appeal for calm alongside cooler heads such as Xu.
Negotiations began at 11am the next day. Weeks later, a deal was announced: Shenzhen would pay silicosis sufferers between US$17,000 and US$35,000 and cover medical costs moving forward. Yet many still are not satisfied.
In the absence of robust courts, China often settles labour disputes this way, says Mary Gallagher, a political scientist at the University of Michigan, in the US. Rural petitioners organise mass, repeated demonstrations; officials hope to appease them with one-off payouts. “But they never acknowledge the systemic failures,” she says.
Clashes between the Hunan petitioners and authorities have continued. Dozens of workers hoping to return to Shenzhen or Beijing to seek more money have been repeatedly intercepted and, on at least one occasion, roughed up by police, petitioners say.
Stricken villages have become closely surveilled. During one trip to Sangzhi county, a Washington Post reporter was surrounded by plain-clothes security officials and forced to leave the province. Authorities harassed villagers who were interviewed during another visit.
Xie Decai, Sangzhi county’s deputy director of propaganda, has denied official wrongdoing and says he has had 10 meetings with villagers.
Justice doesn’t exist in this society. It has glory and wealth and skyscrapers built on our bones
“Some are still unhappy, but it’s not a matter of whether they get compensation, it’s a matter of how much,” Xie says. “As far as we are concerned, the matter is settled.”
The dispute isn’t settled for a Sangzhi county protest leader who sat in a farmhouse plotting his 13th or 14th trip to petition in Shenzhen or Beijing. He got US$24,000 in compensation for silicosis, but the money wasn’t enough to raise his children, says the man, who fears official reprisal and speaks on the condition of anonymity.
“Justice doesn’t exist in this society,” he says. “It has glory and wealth and skyscrapers built on our bones.”
In a picturesque valley across Hunan, Xu, 51, doesn’t speak of compensation. As villagers fell ill one by one over the years, he says, some families begged for help, others cursed him for finding jobs for drillers in Shenzhen.
“I did it with good in my heart,” he says. “How could we have known?”
In the past two years, he has spent US$12,000 feeding and lodging protesters in Shenzhen. He advises families of pneumoconiosis petitioners across the country on WeChat. He checks up on Leiyang widows whose husbands once followed him south to work. He’s still petitioning.
All he wants is a public accounting of the disease by the government, he says, not money.
Xu waves a hand at his big house, at the empty rooms. If he had never found drilling, he says, they might be filled with his brothers, his nieces and nephews.
“It’s conscience.”
Text: The Washington Post