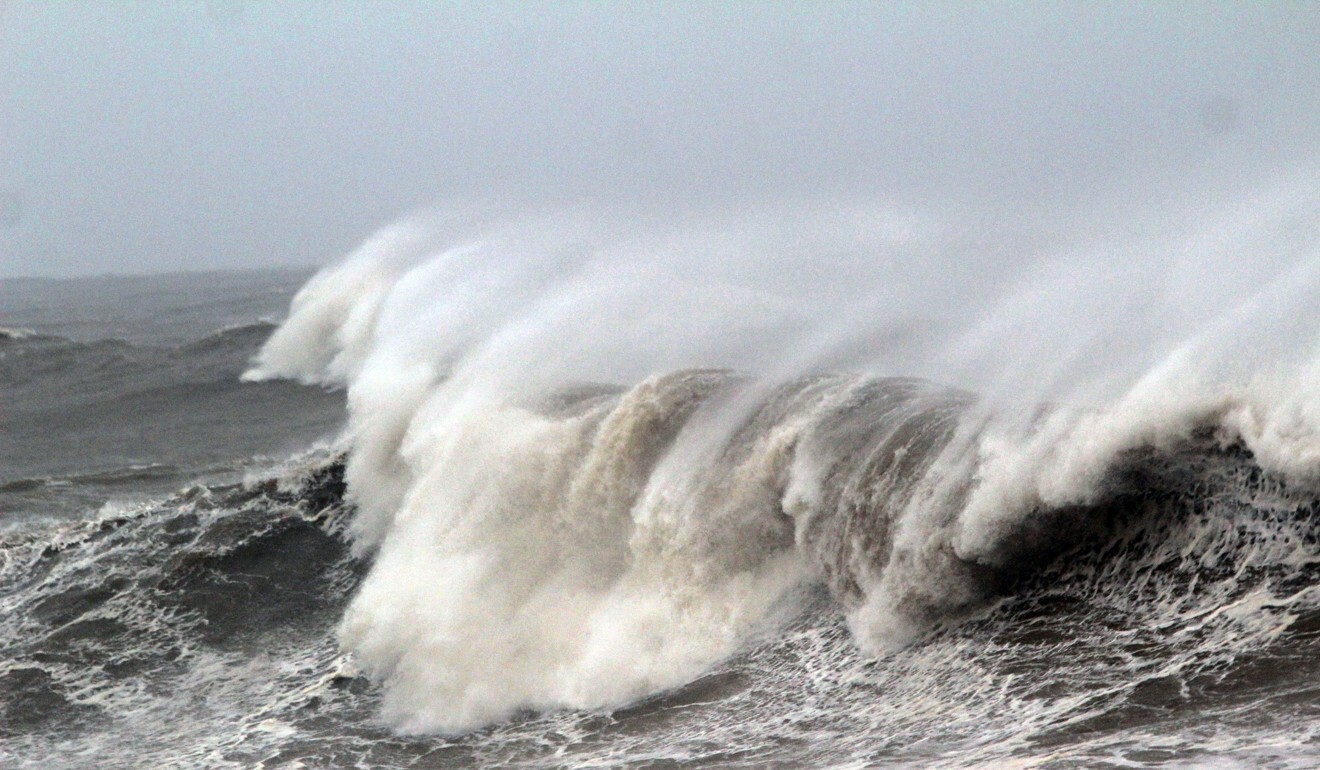

‘Super cyclone’ Amphan batters Bangladesh and India, killing at least 20 as millions flee
- Strongest such storm in decades pounded coast with high winds and heavy rains, leaving trail of destruction
- Authorities evacuated more than three million people, but task was complicated by need to prevent spread of coronavirus
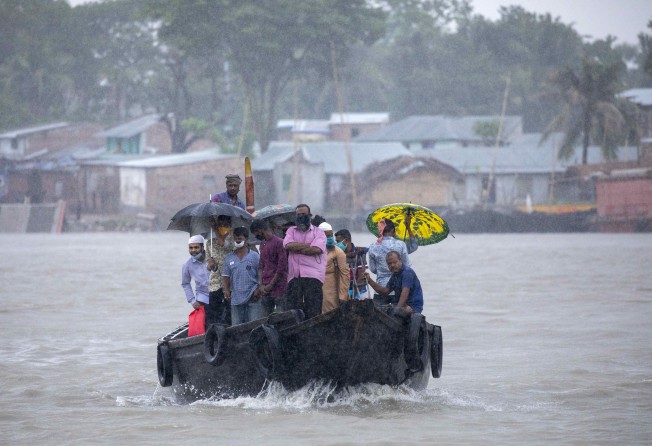

The most powerful cyclone to hit Bangladesh and eastern India in more than 20 years tore down homes, carried cars down flooded streets and claimed the lives of more than a dozen people.
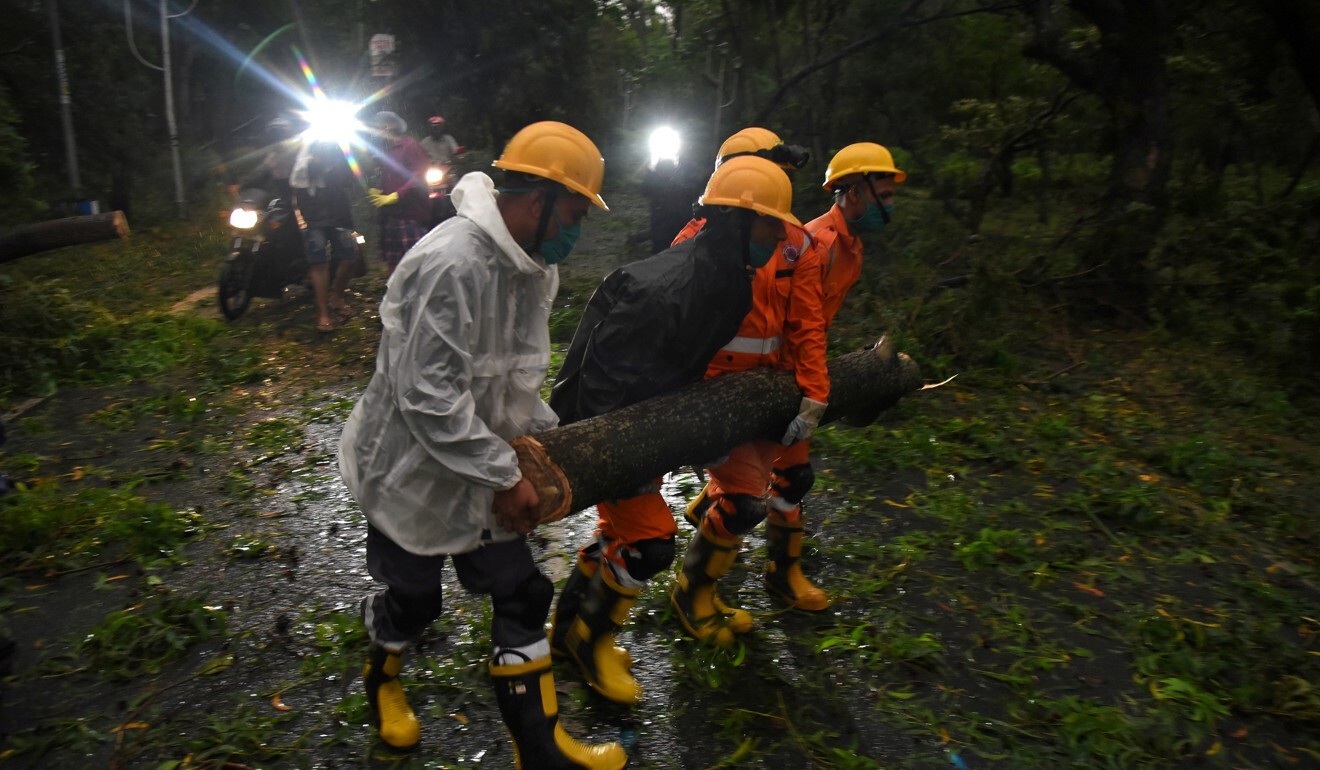
Authorities began surveying the damage on Thursday after millions spent a sleepless night which saw 165kph (100mph miles) winds carrying away trees, electricity pylons, walls and roofs, and transformer stations exploding.
In Bangladesh, officials said they were waiting for reports from the Sundarbans, a Unesco World Heritage Site famed for its mangrove forest and population of endangered Bengal tigers, which bore the brunt of the storm.
Widespread relief that the evacuation of more than three million people from coastal villages had averted the horrific death tolls of past storms was tempered by fears of the coronavirus pandemic spreading in crowded shelters.
Authorities in both countries sent masks and sanitiser but social distancing was virtually impossible as families packed into reinforced schools, government buildings and community halls.

Cyclones are an annual hazard along the Bay of Bengal coast. In 2007, Cyclone Sidr left more than 3,500 dead in Bangladesh.
India’s West Bengal chief minister Mamata Banerjee estimated there were 10-12 deaths in her state, though not all were immediately confirmed. Bangladesh officials said eight people had died, including a five-year-old boy and a 75-year-old man, both hit by falling trees, and a cyclone emergency volunteer who drowned.
Falling trees and chunks of concrete carried by the powerful winds were also blamed for the deaths in India.
West Bengal capital Kolkata awoke to flooded streets with some cars window-deep in water.
Much of the city of 15 million people was plunged into darkness as transformer stations exploded.
Millions across India and Bangladesh were left without power, officials said.
The cyclone weakened as it moved along the Bangladesh coast but still unleashed heavy rains and fierce winds in Cox’s Bazar, the district which houses about one million Rohingya refugees from violence in Myanmar.

Amphan was the first “super cyclone” to form over the Bay of Bengal since 1999, and packed winds gusting up to 185kph at sea.
It brought a storm surge – a wall of ocean water that is often one of the main killers in major weather systems – that roared inland.
In southwest Bangladesh, a 1.5 metre (five-feet) surge broke an embankment and swamped farmland, police said.
Bangladesh officials said the mangrove forests of the Sundarbans had borne the brunt.
“We still haven’t got the actual picture of the damage. We are particularly concerned over some wild animals. They can be washed away during storm surge in high tide,” forest chief Moyeen Uddin Khan said.
Houses “look like they have been run over by a bulldozer”, said Babul Mondal, 35, a villager on the edge of the Indian side of the Sundarbans.
“Everything is destroyed.”
Bangladesh’s low-lying coast, home to 30 million people, and India’s east are regularly battered by cyclones that have claimed the lives of hundreds of thousands of people in recent decades.
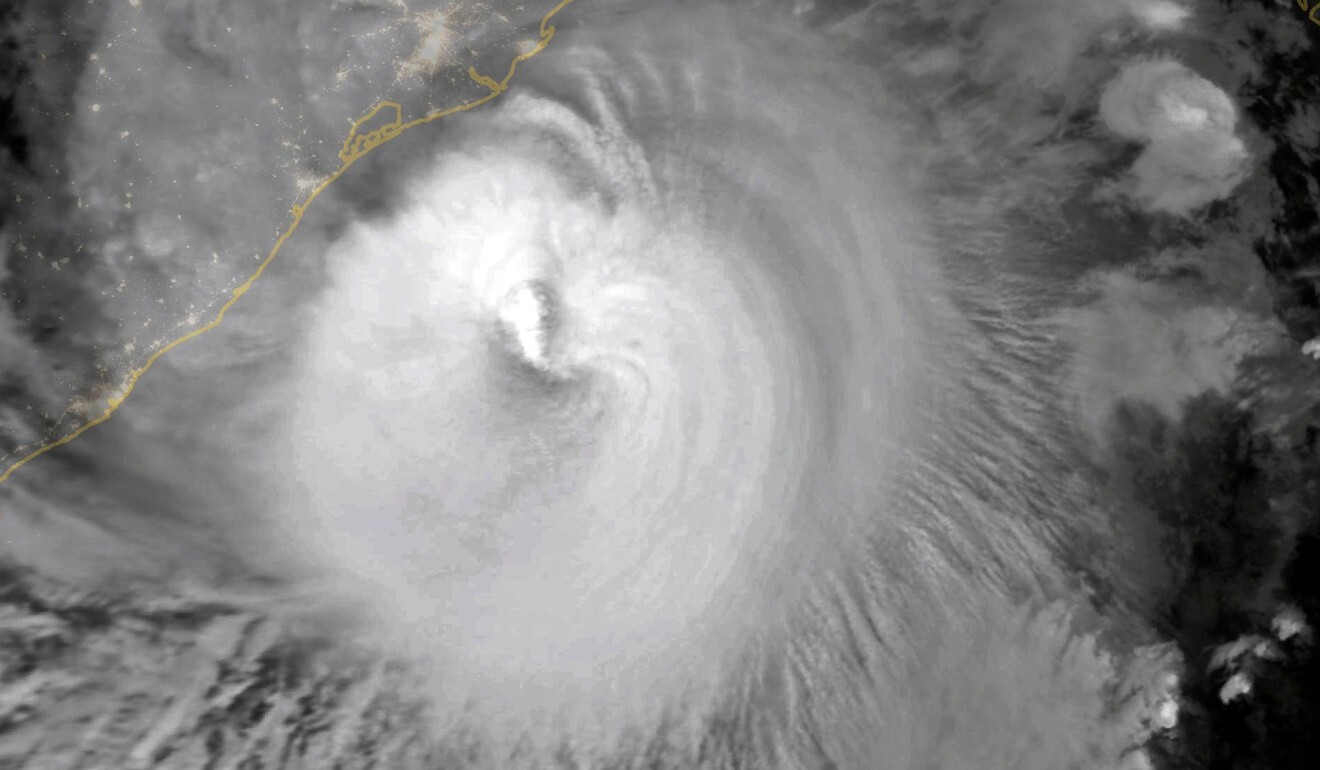
A 1999 super cyclone left nearly 10,000 dead in India’s Orissa state, eight years after a typhoon, tornadoes and flooding killed 139,000 in Bangladesh.
In 1970, half a million perished.
While the frequency and intensity of storms have increased – blamed partly on climate change – casualties have fallen thanks to faster evacuations, better technology and more shelters.
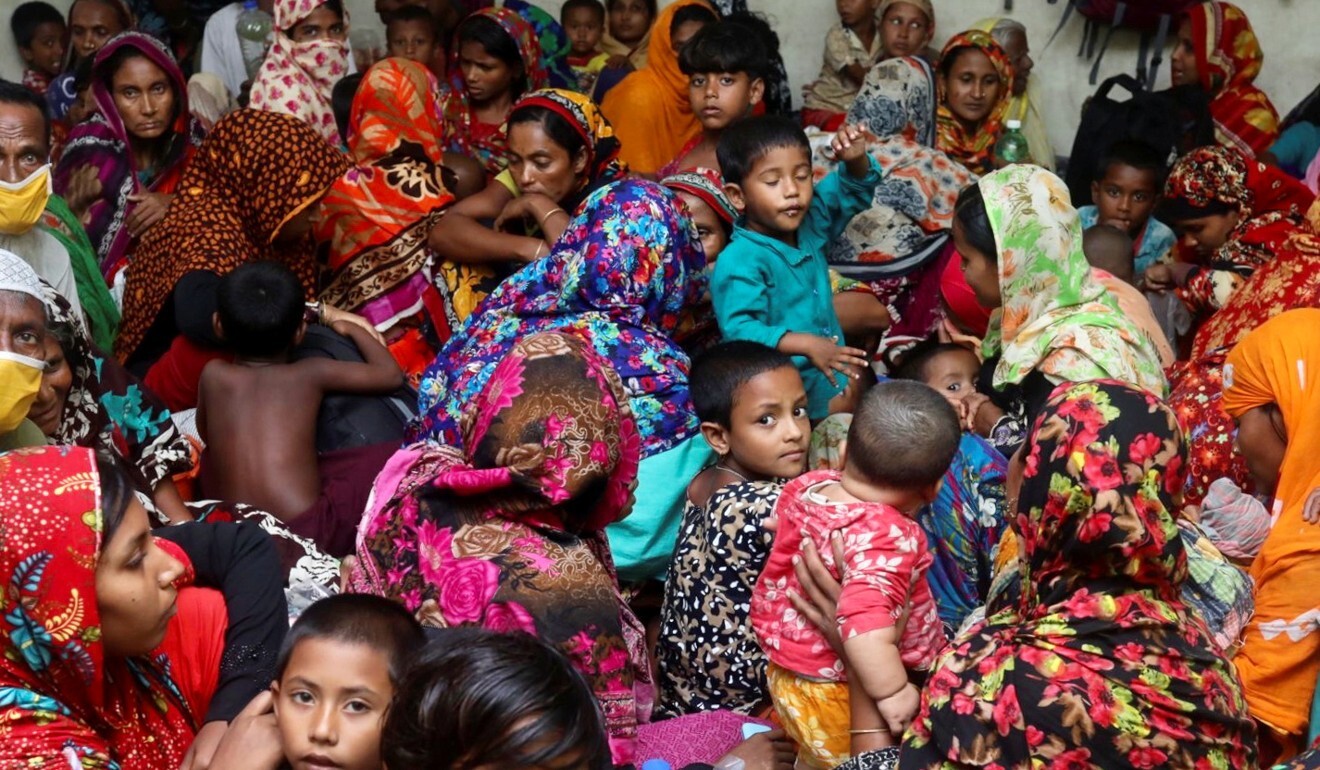

Enamur Rahman, Bangladesh’s junior minister for disaster management, said 2.4 million people and over half a million livestock were brought to shelters.
India evacuated more than 650,000 in West Bengal and Orissa.
Because of coronavirus, authorities used extra shelter space to reduce crowding, while making face masks compulsory and setting aside isolation rooms.
Infection numbers are still soaring in both countries.
Sulata Munda, a villager in Bangladesh, said she and fellow villagers decided not to go to a shelter.
“We fear the cyclone, but we also fear the coronavirus,” the mother of four said.