Central/Eastern Europe and Mexico offer strong incentives for Hong Kong manufacturers to relocate factories
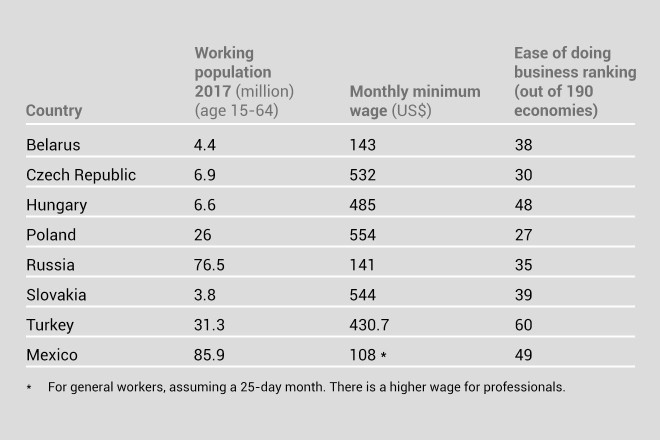
Hong Kong Trade Development Council (HKTDC) provides free research into production sites in Belarus and Russia, as well as Czech Republic, Poland, Hungary, Slovakia, Turkey and Mexico

[Sponsored article]
Hong Kong-based manufacturers have started looking beyond Asian economies to cut costs and diversify their operations geographically. The Hong Kong Trade Development Council (HKTDC) has researched a wealth of reliable information that these manufacturers need to consider.
Economies in Central and Eastern Europe boast highly educated populations and mature infrastructure, while costs are considerably lower than in their Western European peers. These countries at the western end of the Belt and Road offer proximity to high-value Western European markets such as Germany and the United Kingdom.
Emerging markets present pros and cons that manufacturers must weigh up before making their move. In the third of a three-part series, the HKTDC summarises prospects in two former Soviet states – Belarus and Russia – along with the European Union’s Visegrad Four – Czech Republic, Poland, Hungary and Slovakia. The analysis also includes Turkey, which, like Russia, straddles Europe and Asia, and one North American manufacturing powerhouse, Mexico.

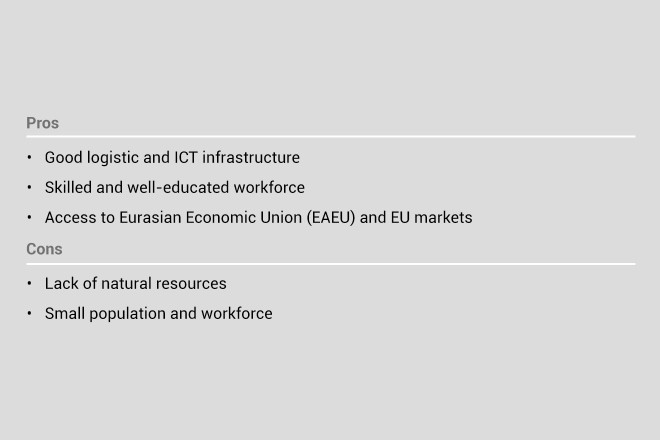
Belarus: industrial hub with a high-tech vision
Belarus has garnered a world-class reputation in various industries, including electronics, light industry (such as textiles, knitting, sewing, footwear and household electrical appliances), machinery and equipment, ICT, chemicals and food processing. A national priority is to develop export-oriented hi-tech industries, such as ICT, logistics, home appliances, electronics and electrical equipment.
Free economic zones (FEZs) – led by China-Belarus industrial park, Great Stone – provide generous investment incentives, including preferential arrangements on corporate income, real estate and land taxes.
Belarus has FEZs in Brest, Gomel, Grodno, Minsk, Mogilev and Vitebsk with general incentives that include: five years’ profit tax exemption following first profit, zero property tax, zero customs duties for imports of raw materials and equipment, 50 per cent VAT discount for the production of import substitution goods, and exemption from paying National Agriculture Support Fund.
Manufacturers interested in investing in Belarus can find out more from the HKTDC article Belt and Road Initiative: The Role of Belarus.
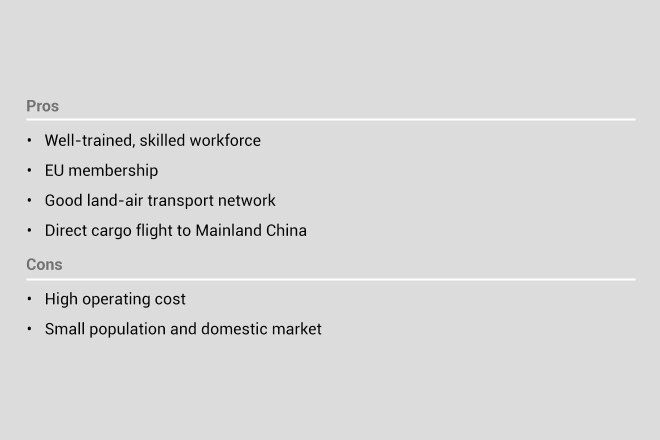
Czech Republic: generous incentives for advanced tech, R&D

A member of the Visegrad Four (V4), Czech Republic industry sectors include electronics, automobiles and auto parts and ICT. High-value industries such as R&D and advanced technology receive generous incentives. It is also home to many world-class engineering services providers, such as MBtech Bohemia and Porsche Engineering Services.
The Czech Republic provides financial support to investments in manufacturing industry, technology centres and business support services centres. This support ranges from 25 per cent of eligible costs of a large enterprise to 45 per cent of the eligible costs of a small enterprise, including fixed assets and two years’ wages of the newly created jobs. Investors could also receive 10-year corporate income tax relief, and cash grants for job creation and training.
Manufacturers interested in investing in the Czech Republic can find out more from the HKTDC’s infographics page and articles The Czech Republic: A Belt and Road Link in CEE, The Visegrad Four (V4) Nations: Early Adopters of the Belt and Road Opportunity, and Belt and Road Opportunities in Central and Eastern Europe.
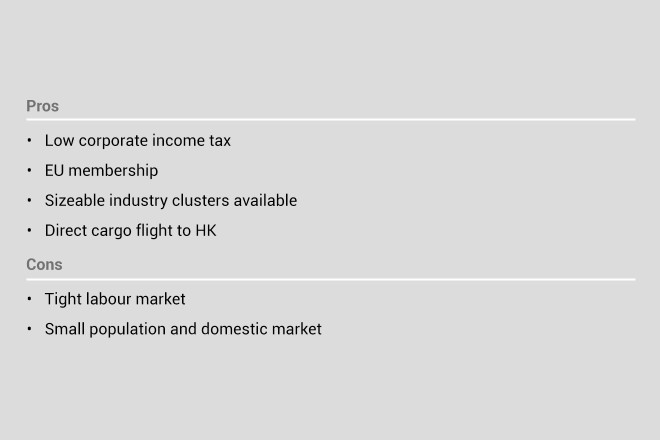
Hungary: largest electronics producer in Central/Eastern Europe

Hungary is a V4 member that manufactures automobiles and parts and is the largest electronics producer in Central and Eastern Europe, representing more than one-fourth of the region’s total electronics output. More than 40 of the top 100 global original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts suppliers have set up in Hungary.
Hungary eliminated free trade zones, but provides incentives such as cash subsidies, development tax allowances, training and job creation subsidies, as well as for investments in manufacturing plants, logistics facilities, services centres, research and development facilities, bioenergy facilities and tourism.
Manufacturers interested in investing in Hungary can find out more from the HKTDC’s infographics page and articles Hungary: Leading the Way in BRI Co-operation, The Visegrad Four (V4) Nations: Early Adopters of the Belt and Road Opportunity, and Belt and Road Opportunities in Central and Eastern Europe.
Poland: 14 special economic zones on major supply routes

The largest member of the V4 Group, Poland’s manufacturing strengths include electronics, electrical appliances, automobiles and parts, and processed food. There is preferential access to domestic and regional consumer markets in the EU and Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). Special economic zones (SEZs) scattered throughout Poland have income tax exemptions, real estate tax exemptions and competitive land prices.

Poland has 14 SEZs along major routes of the supply chain throughout the country that offer residents exemptions from customs duties and VAT, competitive land prices, zero property and income tax, and good access to high-quality local suppliers. Government aid and investment grants are also available in SEZs depending on region, business size and activities performed.
In general, better favour would be given to less-developed regions, small- and medium-sized enterprises, R&D and the use of renewable energy.
Manufacturers interested in investing in Poland can find out more from the HKTDC’s infographics page and articles Poland: Profiting from Increasing Asia-Europe Rail Traffic, The Visegrad Four (V4) Nations: Early Adopters of the Belt and Road Opportunity, and Belt and Road Opportunities in Central and Eastern Europe.
Russia: ready-to-use infrastructure, energy resources

The world’s largest country is an industrial centre for electronics, metal products, automotive, textiles and machinery. Russia is promoting investment in import-substituting industries such as non-ferrous metals, aircraft and components, automobiles, electronics and food machinery. There are SEZs and industrial production (IP) zones across the country that allow cost-savings of up to 30 to 40 per cent through tax and customs incentives, land plots with ready-to-use infrastructure, and free connection to energy resources.
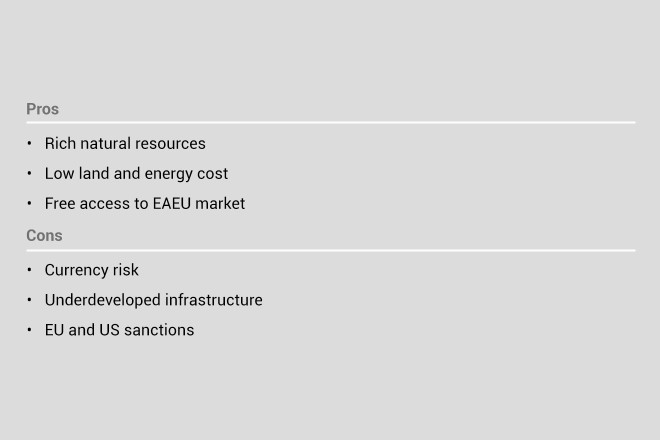
The SEZs, innovation centres and advanced development zones (ADZs) are in different parts of the country and focusing on different industries. General incentives for SEZs include exemption from customs duties and VAT on imports, reduced corporate income tax, reduced property tax, discounts on infrastructure expenses and access to a “One Window” special administrative regime.
Residents of the Skolkovo Innovation Centre (Moscow) are exempted from profit tax, VAT, property tax, customs duties and VAT on imports. General incentives for ADZs that target the Far East and Eastern Siberia include five-year exemptions on profit, land and property taxes.
Manufacturers interested in investing in Russia can find out more from the HKTDC’s infographics page and articles Russia: A Rapidly Developing Belt and Road Technological Partner, Russia: A Prime Belt and Road Investment Destination, and Russia: World Cup, International Sanctions.
Slovakia: magnet for automotive and electronics industries

V4 member Slovakia boasts the highest per-capita car production in the world and has become a magnet for export-oriented manufacturing industries, such as automotive and electronics, as well as a hotspot for shared services centres (SSCs) and business process outsourcing centres (BPOs). The Slovakian government is stretching its wings to Asia, with initiatives such as a plan to start a double tax treaty negotiation with Hong Kong.

Slovakia provides incentives to investments in industrial production, technology centres and business service centres. The value varies across the regions and sectors, while the less-developed regions generally enjoy preferential treatment. The incentives could be in the form of income tax relief, lower property prices, a cash grant for the acquisition of material assets and immaterial assets, or contribution for job creation.
Manufacturers interested in investing in Slovakia can find out more from HKTDC articles Slovakia: An Emerging Hub on the New Silk Road, The Visegrad Four (V4) Nations: Early Adopters of the Belt and Road Opportunity, and Belt and Road Opportunities in Central and Eastern Europe.
Turkey: ambitious incentive programmes

Turkey’s suitable industries include electronics and electrical appliances, textiles, garments, auto parts, and processed food. Located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, the Middle East and Africa, Turkey has long been a strategic hub for global trade, logistics and manufacturing. Import-substituting industries, such as machinery, transport equipment and chemicals enjoy favourable government incentives – including exemptions from VAT and customs duty, social security and interest rate support and land allocation.

Turkey has 17 free zones throughout the country and two ambitious programmes, namely the “Investment Incentive Programme” and the “Project-Based Incentive Scheme”, which offer different incentive packages. The free zones provide an exemption from VAT, customs duty, and stamp duty. Manufacturing companies are also free from corporate income tax.
Local and foreign investors can be eligible for various support measures – according to investment size, region, sector and product – that include VAT exemption, customs duty exemption, tax deduction, social security premium support for employer’s share, interest-rate support, land allocation and VAT refund.
In the least-developed region of Turkey (Region 6 – Eastern Anatolia, adjacent to Armenia and Iran), income tax withholding support and social security premium support for the employee’s share are also available.
Manufacturers interested in investing in Turkey can find out more from the HKTDC articles Turkey: A Strategic Trade-Manufacturing-Investment Nexus, Turkey’s Competitive Incentive Schemes, and Turkey: A Strategic Trade-Manufacturing-Investment Nexus.
Mexico: four free-trade zones, reduced bureaucracy

This bridge between the US and Latin America is a hub for industries such as electronics, electrical appliances, automobile and auto parts, textiles, garments and processed food. A higher regional value content requirement for apparels and automobiles to enjoy duty-free access to the US and Canadian markets is required under the USMCA. The President-elect has promised reforms in the areas of energy, education, security and public spending on social programmes and infrastructure, plus a commitment to combat corruption and violence.

Mexico has four free-trade zones (FTZs) at San Luis Potosi, Mexico City, Monterrey and Guanajuato, which are open to all industries that offer lower customs duties, delayed payment of tariffs, reduced bureaucracy for exports and imports and local access to customs officers. Mexico’s IMMEX incentive programme allows exemption from import tax and deferred customs duties payments.
Manufacturers interested in investing in Mexico can find out more by reading the HKTDC articles From NAFTA to “NAFTA 2.0”, and U.S. and Canada Reach Deal on New Tri-lateral Trade Agreement.
Check out the full HKTDC overseas manufacturing report.







