Advertisement
Nvidia hedges against cryptocurrency hangover with new line of chips just for miners
- Nvidia has created a new line of chips, called CMPs, exclusively for cryptocurrency miners
- It has also limited the so-called hash rate on its newest graphics chips for video gaming, making them inefficient for cryptocurrency mining
Reading Time:5 minutes
Why you can trust SCMP
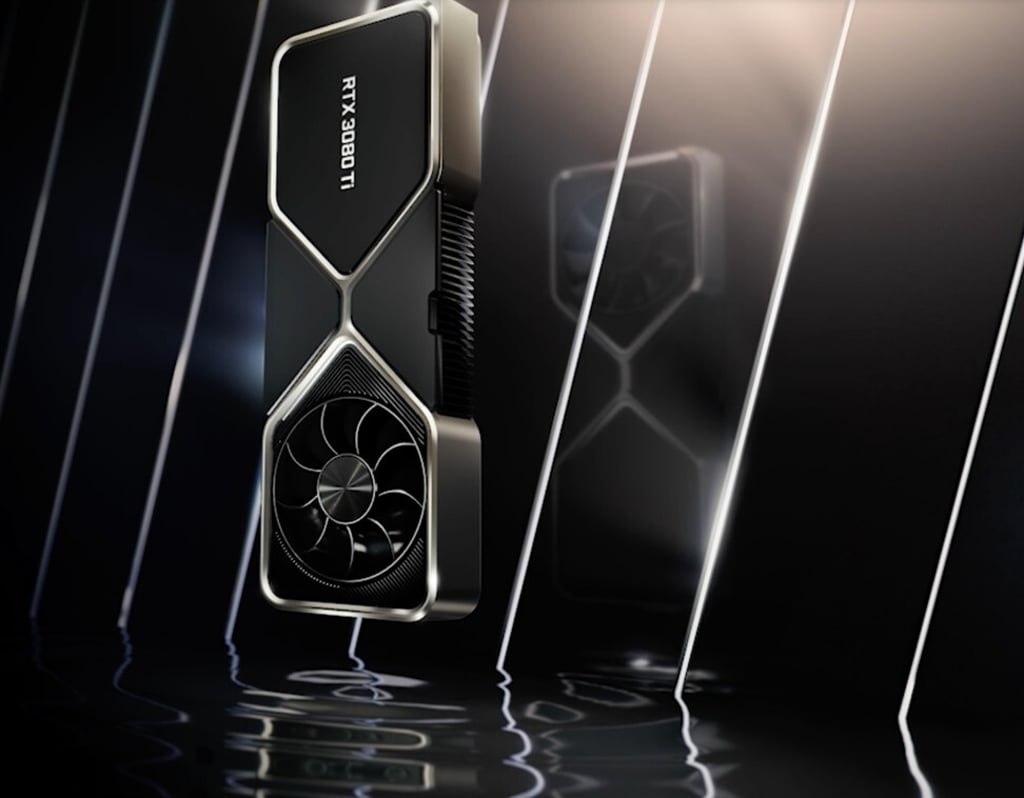
Nvidia Corp has an unlikely message for some of its most voracious customers: please do not buy our latest high-end computer-graphics chip.
The GeForce RTX 3080 Ti, a US$1,199 graphics card, and the RTX 3070 Ti, which costs about half that amount, have had some of their capabilities deliberately stripped out. Nvidia wants them to be the exclusive preserve of its core video gaming customer base and is nixing the products’ ability to effectively mine cryptocurrencies like bitcoin and ethereum, seeking to discourage miners from snapping up all the supply to build massive crypto-processing farms.
Instead, Nvidia is pushing a chip just for the miners. The company’s extreme action is one result of the rising influence of cryptocurrencies, touching on the retail market, the environment, and the worlds of finance and technology.
Advertisement
Virtual currencies have been in the news as the preferred ransom payment method of cyber attackers. Elon Musk tweets about them more often than he does about his electric car company, Tesla. And as they attract new investors and participants daily, cryptocurrencies have grown more unpredictable and hungrier for the hardware used to generate them.
Nvidia chief executive Jensen Huang is swimming against this cryptocurrency tide. His company needs to avoid a repeat of the 2017 run-up in demand for its graphics chips, which are the most efficient off-the-shelf semiconductors for solving math problems to create the codes that are the basis of cryptocurrencies.
Advertisement

Advertisement
Select Voice
Select Speed
1.00x