An astronaut in space has recorded a ‘first of its kind’ video of mysterious blue jets
European astronaut films storms from the International Space Station using a special camera
We’re used to lightning that shoots down from clouds, but a lesser-known form of electricity blasts up from cloud tops — and out toward space.
Called blue jets, these gigantic electrical discharges are rarely photographed. Typically, only pilots who fly over active thunderstorms see or photograph them. Satellites have recorded them, too, but not very well.
However, an astronaut in space has recorded a first-of-its-kind color video of elusive blue jets, according to a January 2017 study in Geophysical Research Letters.
Researchers behind the study asked European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Andreas Morgensen to perform the “Thor experiment,” named after the Norse god of lightning, back in 2015. His mission: film thunderstorms from the International Space Station (ISS), located some 250 miles above Earth, with a very sensitive video camera.
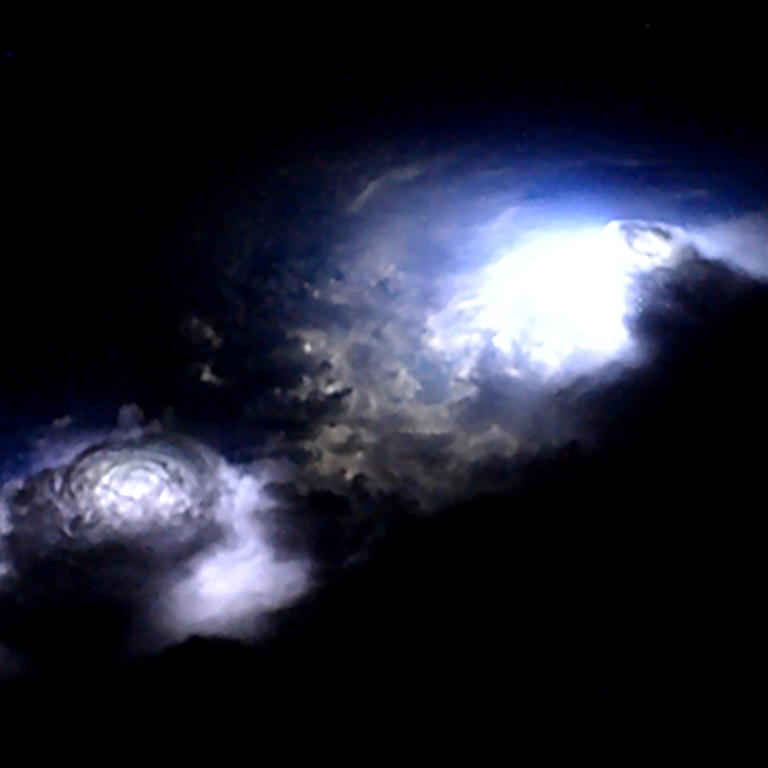
Morgensen ended up filming a particularly active storm cell over India’s Bay of Bengal, and in the footage he managed to catch this oddity:

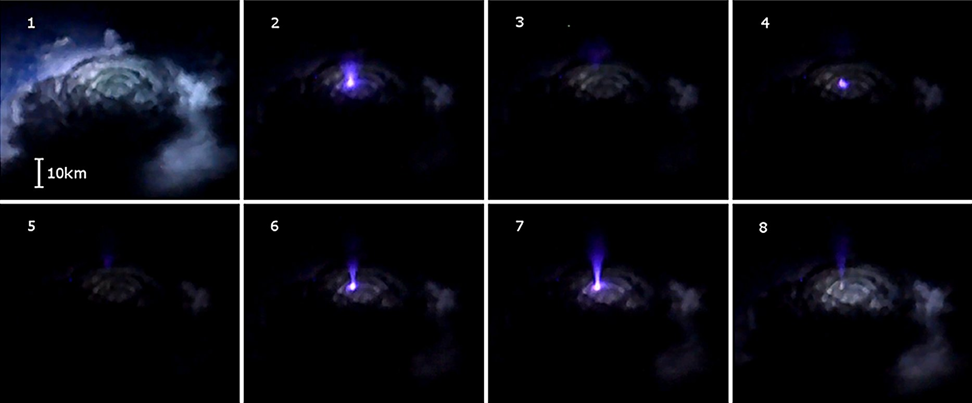
If you missed it, below is a still-image breakdown of the thunderstorm.
Right after lightning from below the storm illuminates the clouds, you can see a the blue-purple cone of a blue jet pulsate a little, then finally shoot out of the cloud tops.
It rises more than 10 kilometers (6 miles) high, and then fades away:
Here's a close-up of the blue jet that Mogensen recorded:
Blue jets move at speeds of more than 220,000 mph (360,000 kph), according to the Geophysical Institute at the University of Alaska Fairbanks.
They fan out like cones as they move up, at least until they reach a height of roughly 30 miles (50 kilometers) — halfway to the edge of space — at which point they vanish.
It’s devilishly hard to photograph blue jets and their higher-altitude cousins, red sprites. In fact, researchers have been studying them closely only since the 1990s.
But Morgensen nailed his mission to document them.
“The observations [...] are the most spectacular of their kind,” the researchers wrote, noting this was thanks to an unusually active thunderstorm, the astronaut’s viewing angle, and the high resolution of his camera. “They reveal new aspects of discharge processes at cloud tops, including a pulsating blue jet[.]”
Blue jets aren’t just a curious phenomenon. Like red sprites, they could play a vital role in shaping the air we breathe by combining and breaking apart different types of atmospheric molecules.
But for now “it’s something that we know very little about,” Morgensen said in an ESA video.
The astronaut says a follow-up mission, called the Atmosphere-Space Interactions Monitor, will soon launch to the space station and more closely study blue jets and other high-altitude phenomena, including meteors.