Topic
DiDi operates the dominant ride-hailing app in China and operates elsewhere in Asia-Pacific as well as in Latin America and other regions. It offers other mobility-related services including taxi-hailing, chauffeur-rental, carpooling, bike-sharing as well as food and freight delivery. The company conducted an IPO on the New York Stock Exchange in 2021 amid concerns over national security by the government, which was followed by an order by Chinese regulators for its apps to be removed from app stores in China. In early 2023, the apps returned to app stores after the company delisted itself from the NYSE the previous year.
Allowing the resumption of cross-border data transfers in day-to-day business shows pragmatism can still prevail in Chinese policymaking.
The city’s global financial status is expected to play a big role as companies such as Didi make a homecoming with listings here
As the company quits New York to prepare for a blockbuster relisting, Hong Kong has to make sure it gets the balance right to ensure that other China firms follow.
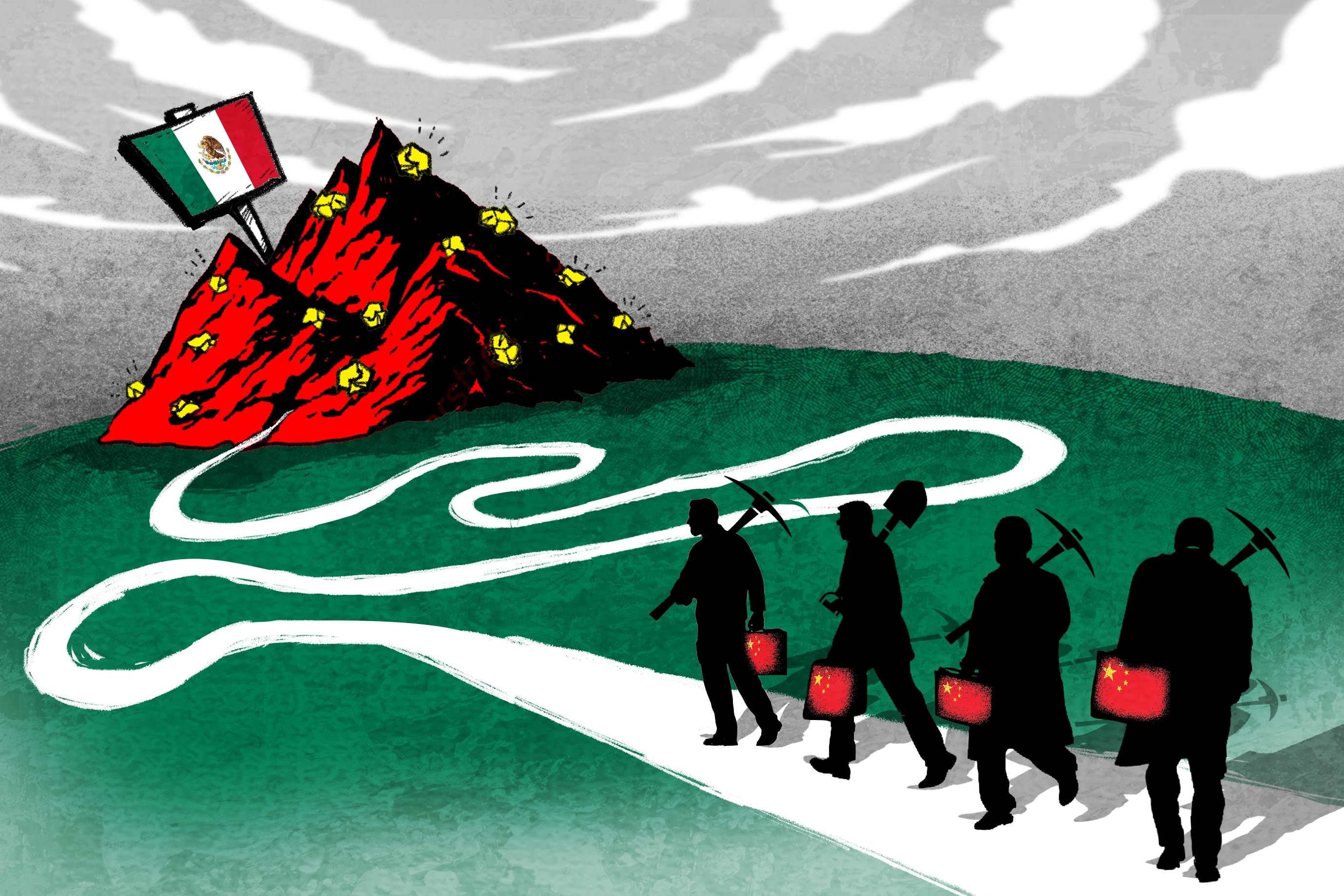
- Seeking economic opportunity, Chinese merchants build bustling markets, sell Made in China goods and deal with occasional resistance from Mexican vendors
- Along with the migrant influx, Chinese brands including DiDi and BYD are gaining greater exposure in Mexico
The global automotive industry is making a “strategic transformation” towards electrification, said Gou Ping, vice-chairman of the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission.
Platforms should send app notifications to remind workers to take a break if they have been working longer than the hours agreed, according to new government guidelines.
The companies will work together to build out battery-swapping stations, which have been growing more rapidly than fixed charging in China.
Readers discuss the regulatory quagmire facing ride-railing operators in Hong Kong, and the need to review taxi driver performance.
Alibaba has cut its GoGoX stake four times over the past two months, as the Hong Kong logistics services firm faces cutthroat competition and regulatory pressure in the mainland’s intracity delivery courier market.
A handful of Chinese technology start-ups are poised to go public during 2024 or early 2025, with most of these firms looking to make their trading debut in Hong Kong.
China’s largest ride-hailing service said it will carry out ‘in-depth technical risk identification and upgrade work’ to fully ensure service stability.
The disruptions affected some of the app’s 400 million users, as well as drivers across China, including in Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou.
Valued at more than US$60 billion, Shein is expected to become the most valuable China-founded company to go public in the US since Didi Global’s debut in 2021 at a US$68-billion valuation.
The company has also announced a plan to buy back up to US$1 billion of its shares amid reports of a planned Hong Kong listing.
Once valued at US$47 billion, WeWork’s plunge into bankruptcy damaged the professional reputation of SoftBank’s Masayoshi Son far beyond the US$11.5 billion he lost in the co-working office space start-up.
How do you get a visa to Shenzhen? How do you pay for everything without cash? Everything you need to know, download and use before, during and after entering the Chinese city from Hong Kong.
Didi posted a 52.6 per cent year-on-year jump in second-quarter revenue to US$6.6 billion on the back of strong demand at both its core mainland China and international operations.
The US$744 million deal enables Xpeng to take advantage of Didi’s business platforms for promotion while helping Didi dodge the cutthroat EV market, an analyst says.
The slowing economy has resulted in a flood of new gig workers who have been reduced to working longer to get fewer orders than they saw during the pandemic.
Since Beijing quashed Ant Group’s IPO in November 2020, a Big Tech crackdown spanning more than two years has left no big industry player unscathed.
Didi recorded a net loss of US$166 million in the first quarter, a significant improvement from its US$2.3 billion loss in the same period last year.
Big Tech firms from Tencent to ByteDance helped create millions of vloggers, content writers and e-commerce sellers amid a slow pandemic-stricken economy.
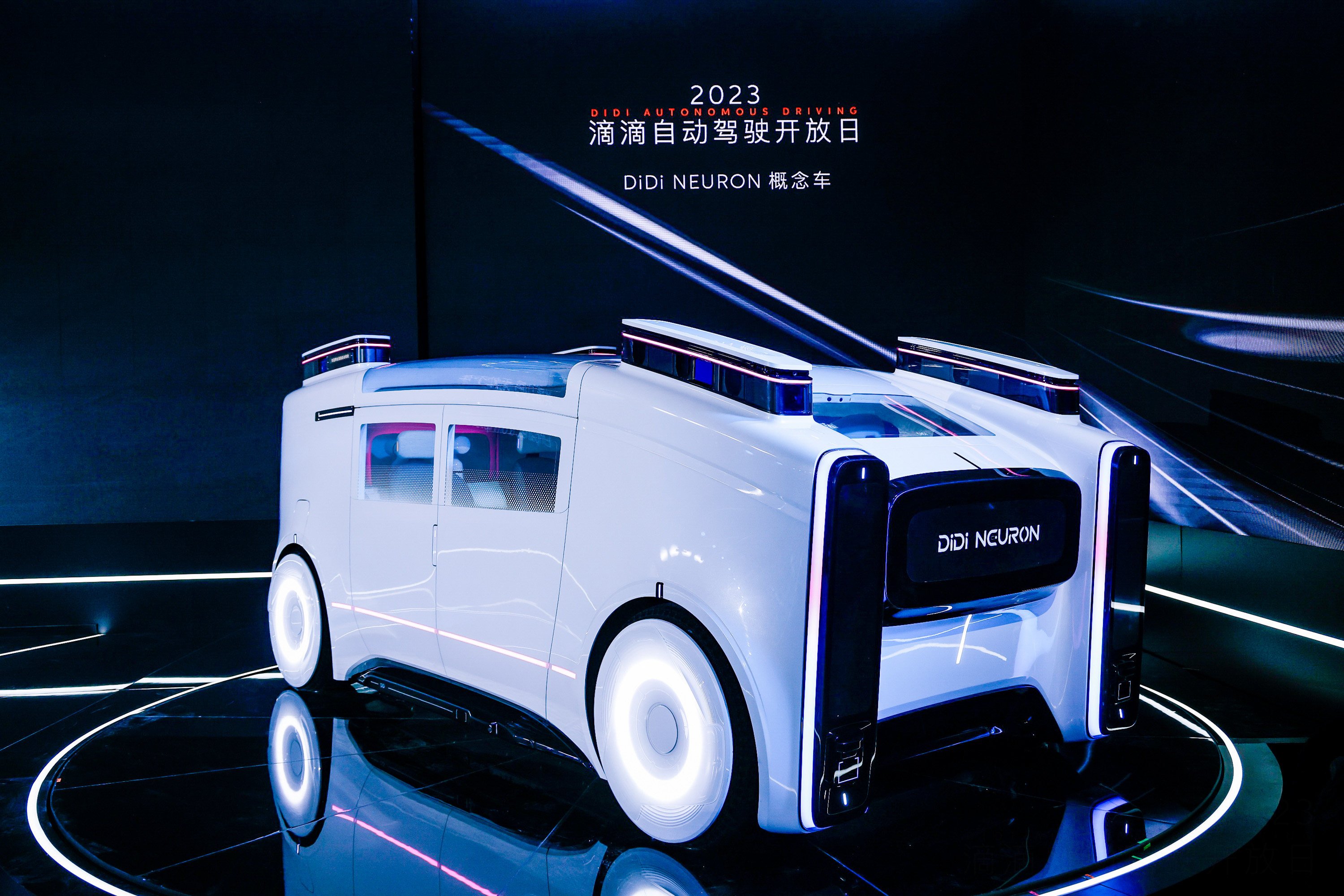
Didi has been preparing for a comeback with autonomous driving cars, a sector favoured by the government, after a 2021 crackdown.
The Beijing-based company has released its first annual report since it delisted from the New York Stock Exchange last year.
Didi’s push into autonomous driving dates back to 2016 when it set up a dedicated unit, and the robotaxi concept car comes after years of research and development.
Micron Technology, the United States’ largest memory chip maker, has become the first foreign semiconductor company to be put under a cybersecurity review by China.
Micron has previously warned investors of the risks of being excluded from the China market.
The reorganisation is in line with e-commerce giant Alibaba’s efforts to stay competitive in China’s vast on-demand local services market, which is dominated by Meituan.
Didi founder and CEO Cheng Wei made his first appearance at the symposium since China launched a cybersecurity probe into the firm in 2021, as Beijing eases its restrictions on the tech sector.
Job cuts at Pakistan-based e-commerce firm Daraz follow a workforce reduction of more than 15,000 at parent Alibaba in the first nine months of 2022.
It marks a crucial step for the company to fully resume its business after Beijing banned it from registering new users for 18 months.