Advertisement
Advertisement
TOPIC
Quantitative Easing
Quantitative Easing
Quantitative easing (QE) refers to large-scale asset purchases by the US Federal Reserve to inject liquidity in the world’s biggest economy after the onset of the global financial crisis in late 2008. In September 2012, stubbornly high US unemployment and faltering economic growth prompted it to launch QE3, under which it planned to buy US$40 billion worth of bonds per month, with no set end date. As of late 2012, it had bought some US$2.3 trillion in long-term securities. In December 2012 it announced it was increasing its purchases to US$85 billion a month.
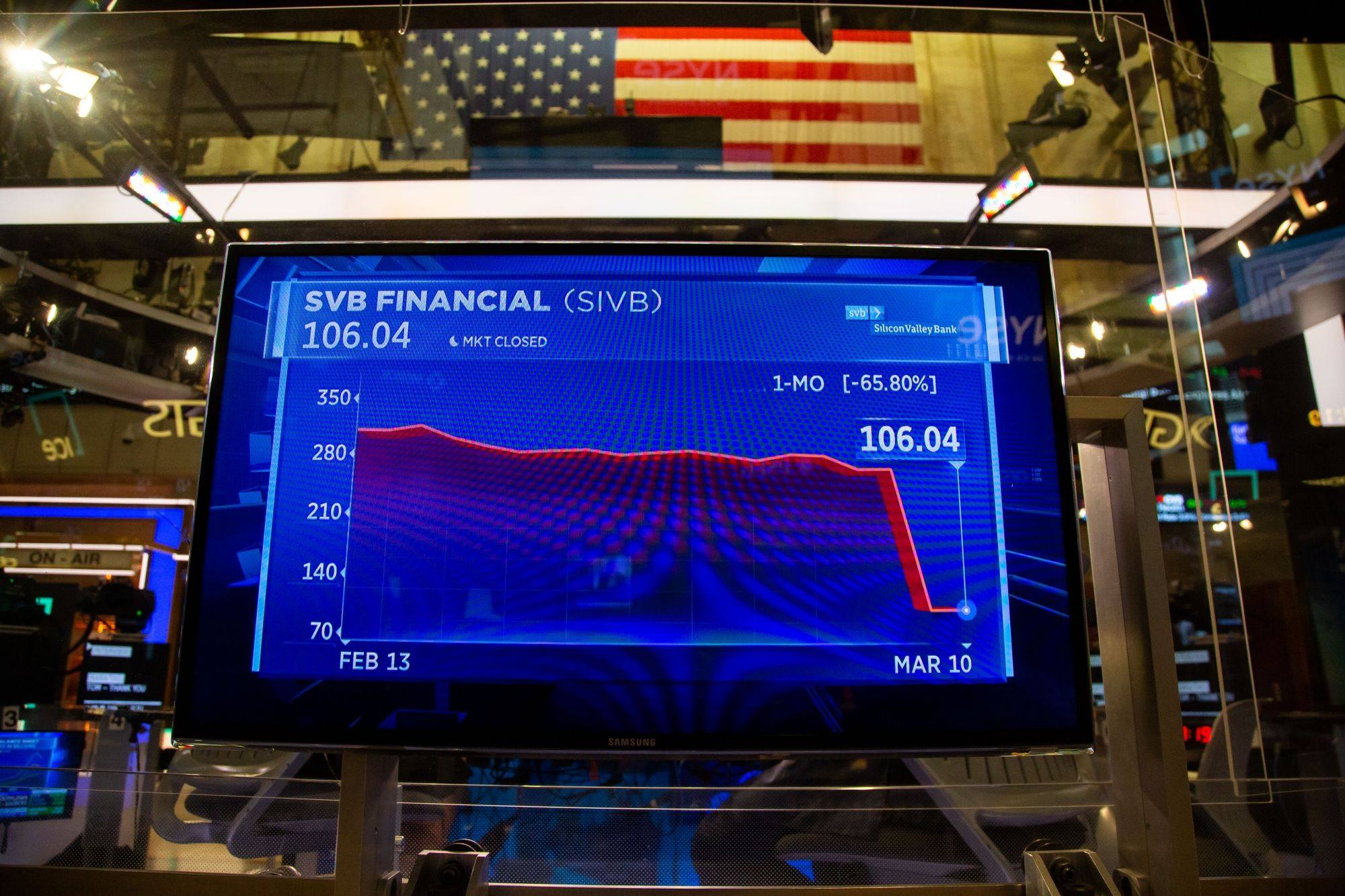
Macroscope | No repeat of the 2008 global financial crisis but other dangers lurk
In the US, large banks remain safe but there is little political appetite to throw fiscal support at the smaller, failing banks. In Europe, the shock that Credit Suisse’s AT1 bondholders were made to absorb losses first, continues to reverberate.
Help preserve 120 years of quality journalism.
SUPPORT NOWAdvertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement